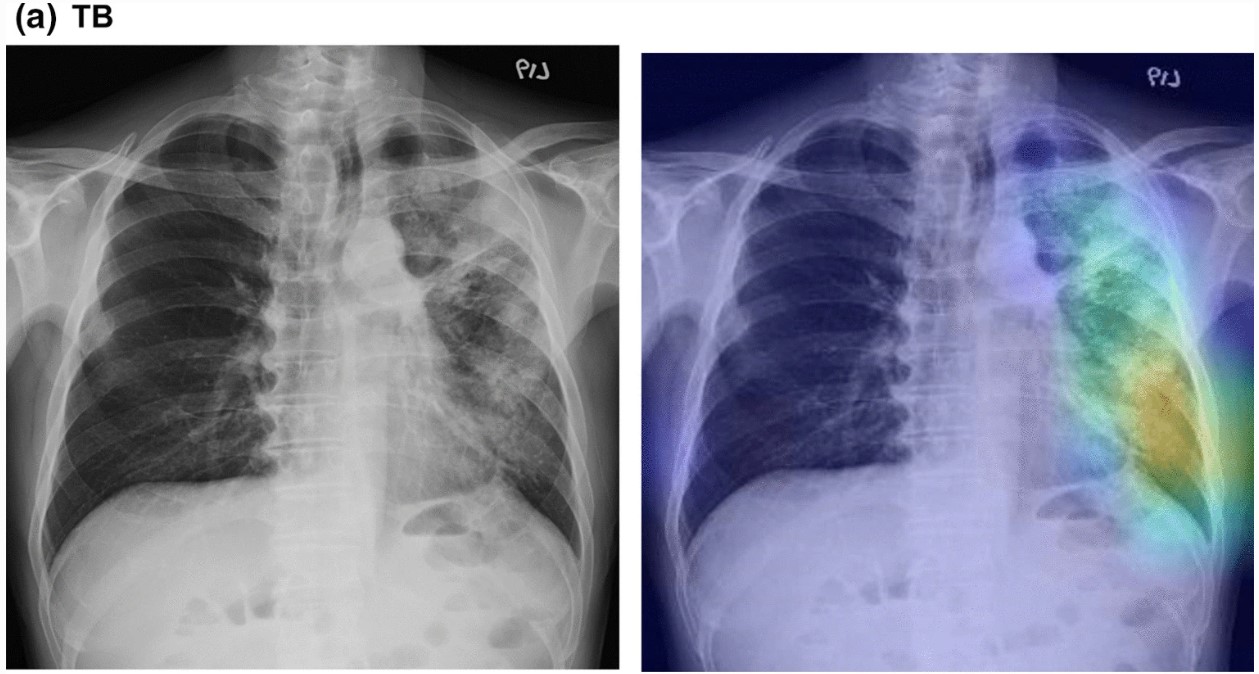
The authors of this study aimed to evaluate whether artificial intelligence, specifically a deep neural network (DNN), was able to distinguish between tuberculosis (TB) or nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease (NTM-LD) patients through chest X-rays (CXRs) from suspected mycobacterial lung disease. A total of 1,500 CXRs from two hospitals were retrospectively collected and evaluated. They determined that the developed DNN model showed satisfactory performance and had higher accuracy than pulmonologists when classifying patients with presumptive mycobacterial lung diseases.
Key points
- The DNN model showed significantly higher classification accuracy compared to pulmonologists.
- The DNN model has stable performance in different mycobacteria prevalence scenarios.
- DNN model could be a screening tool for mycobacterial lung diseases.
Authors: Chia-Jung Liu, Cheng Che Tsai, Lu-Cheng Kuo, Po-Chih Kuo, Meng-Rui Lee, Jann-Yuan Wang, Jen-Chung Ko, Jin-Yuan Shih, Hao-Chien Wang & Chong-Jen Yu