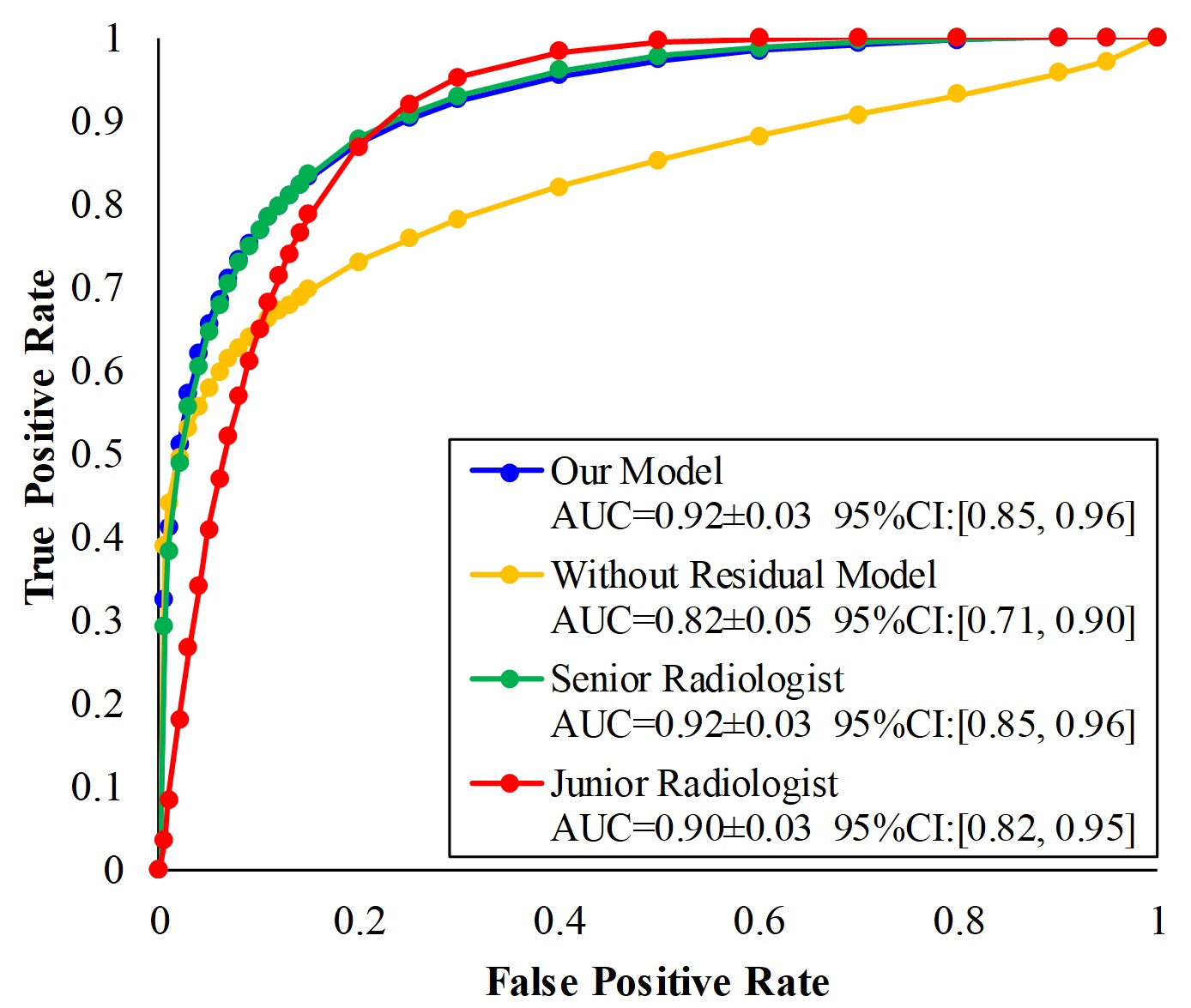
In this study, the authors aimed to develop a deep learning-based artificial intelligence (AI) scheme in order to predict the likelihood of the ground-glass nodule (GGN) being invasive adenocarcinoma that is detected in CT images. The study also compares the accuracy of the AI scheme with the predictions of two radiologists. The study results showed that using an AI scheme improves the performance in predicting invasive adenocarcinoma, and which may also help to improve the development of a more effective personalized cancer treatment.
Key points
- The feasibility of using a deep learning method to predict the likelihood of the ground-glass nodule being invasive adenocarcinoma.
- Residual learning–based CNN model improves the performance in classifying between IA and non-IA nodules.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) scheme yields higher performance than radiologists in predicting invasive adenocarcinoma.
Authors: Jing Gong, Jiyu Liu, Wen Hao, Shengdong Nie, Bin Zheng, Shengping Wang & Weijun Peng