As computational capabilities in healthcare continue to advance, the realm of texture analysis within medical imaging, known as radiomics, offers a promising avenue for uncovering novel imaging biomarkers aiding precision medicine [1].
Nevertheless, clinical translation faces significant hurdles, primarily stemming from the heterogeneity of research questions and inconsistent quality of radiomics reporting, leading to a scarcity of studies that are comparable, reproducible, or generalizable [2]. This challenge is exemplified in our systematic review focusing on radiomics biomarkers in post-radiation stage III/ IV non-small cell lung cancer [3].
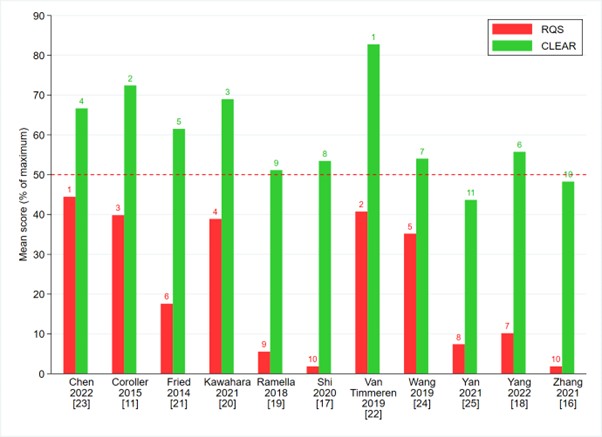
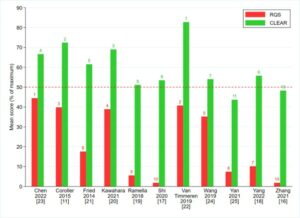
Among the commonly utilized tools for radiomics assessment are the well-established Radiomics Quality Score (RQS) [4] and the CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics (CLEAR) frameworks [5]. In our investigation, we amalgamated these frameworks into a singular comprehensive checklist, denoted as CLEAR-RQS, aiming to enhance standardization and clarity. However, our evaluation of RQS, CLEAR, and CLEAR-RQS unveiled significant variability in radiomics reporting quality, resulting in notable disparities in article rankings.
A recent addition to the landscape is the METRICS (METhodological RadiomICs Score) framework, developed by an international panel through Delphi consensus and endorsed by the European Society of Medical Imaging Informatics (EuSoMII) [6]. This newly introduced scoring tool holds promise as an enhanced approach to assessing radiomics methodologies.
The existence of multiple frameworks catering to radiomics researchers and educators instills optimism for expediting the translation of radiomics into clinical practice by offering avenues for refining methodologies, developing standardization, and fostering collaboration, all essential for driving progress and ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
- Limkin, E.J., et al., Promises and challenges for the implementation of computational medical imaging (radiomics) in oncology. Annals of Oncology, 2017. 28(6): p. 1191-1206.
- Malcolm, J.A., et al., Current state of radiomic research in pancreatic cancer: focusing on study design and reproducibility of findings. Eur Radiol, 2023. 33(10): p. 6659-6669.
- Tran, K., et al., Post-radiotherapy stage III/IV non-small cell lung cancer radiomics research: a systematic review and comparison of CLEAR and RQS frameworks. Eur Radiol, 2024.
- Lambin, P., et al., Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2017. 14(12): p. 749-762.
- Kocak, B., et al., CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): a step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging, 2023. 14(1): p. 75.
- Kocak, B., et al., METhodological RadiomICs Score (METRICS): a quality scoring tool for radiomics research endorsed by EuSoMII. Insights into Imaging, 2024. 15(1): p. 8.
Key points:
- There is heterogenous and low radiomics research quality in postradiotherapy stage III/IV nonsmall cell lung cancer.
- Barriers to reproducibility are small cohort size, nonvalidated studies, missing technical parameters, and lack of data, code, and model sharing.
- CLEAR (CheckList_for_EvaluAtion_of_Radiomics_research), RQS (Radiomics_Quality_Score), and the amalgamated CLEAR-RQS tool are useful frameworks for assessing radiomics research quality and may provide a valuable resource for educational purposes in the field of radiomics.
Authors: Kevin Tran, Daniel Ginzburg, Wei Hong, Ulrike Attenberger & Hyun Soo Ko