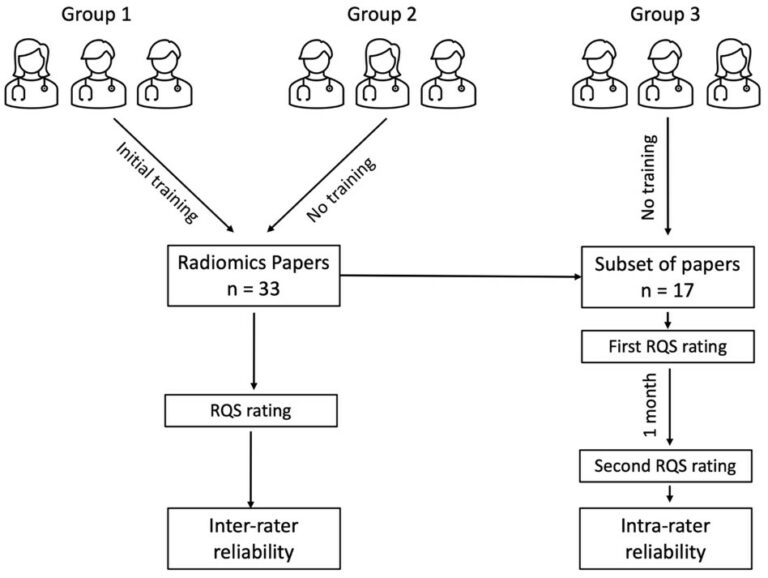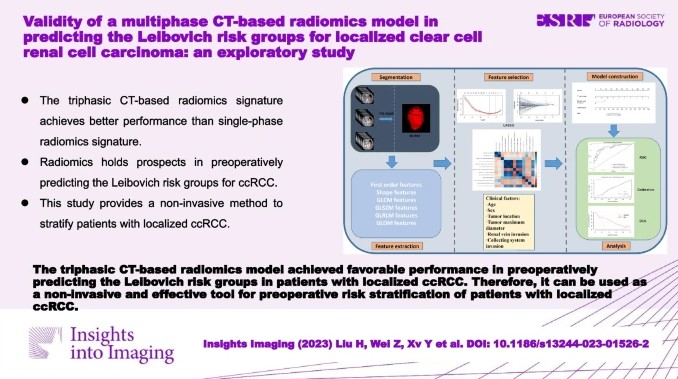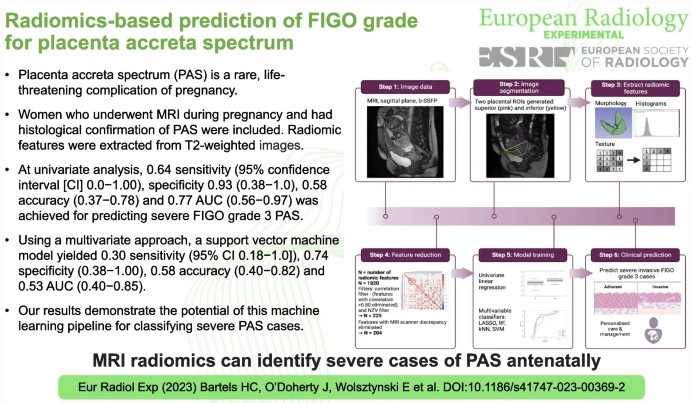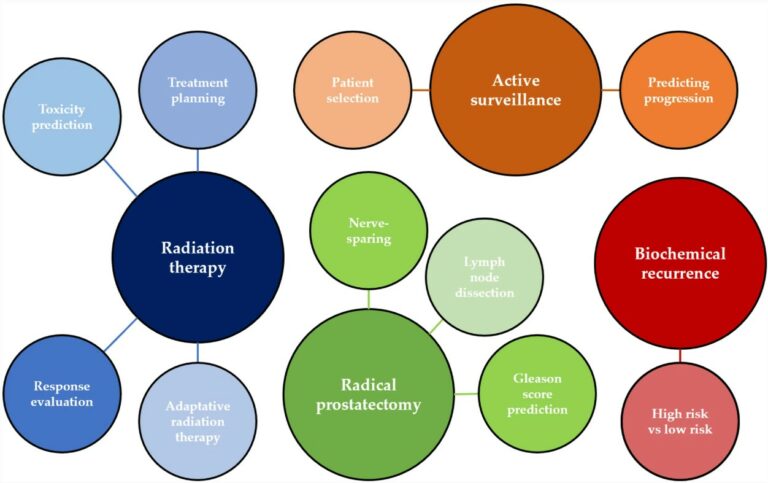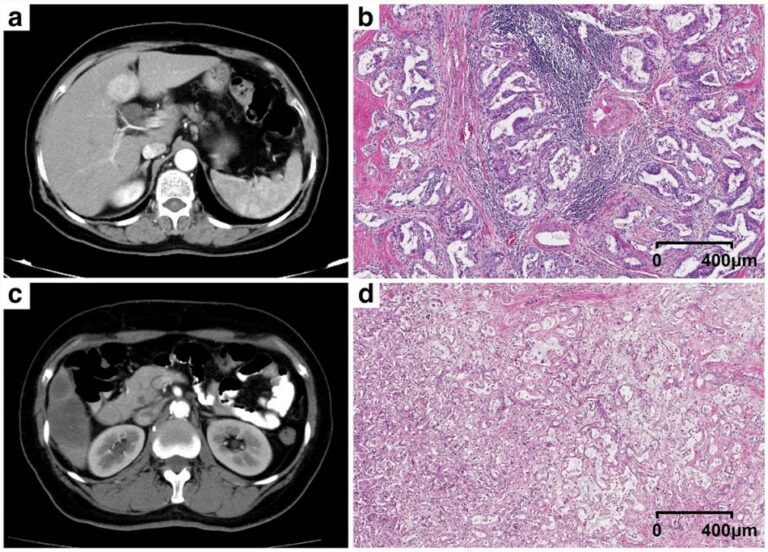
Predicting tertiary lymphoid structures status of ICC patients using CT radiomics
The authors of this study used preoperative CT radiomics in order to predict the tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) status and recurrence-free survival (RFS) of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patients. Enhanced CT images from a total of 116 ICC patients were included when using the radiomics model. The study results showed that the radiomics nomogram displayed better performance in predicting TLSs than