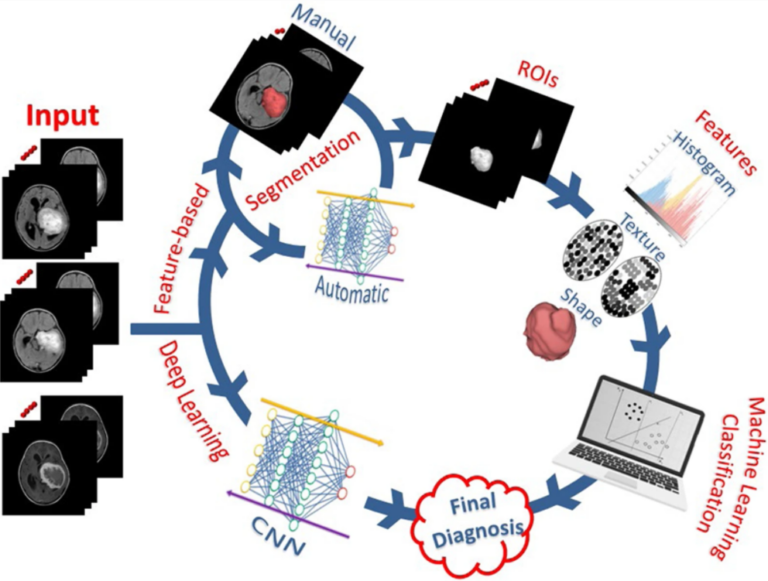
Clinical applications of AI and radiomics in neuro-oncology
In this educational review, the authors take a comprehensive look at various aspects and applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of neuro-oncology, including machine learning, deep learning, and radiomics. The merits and challenges of the deployment and use of AI tools in neuro-oncology are put under the microscope, with the authors concluding that AI has a promising future