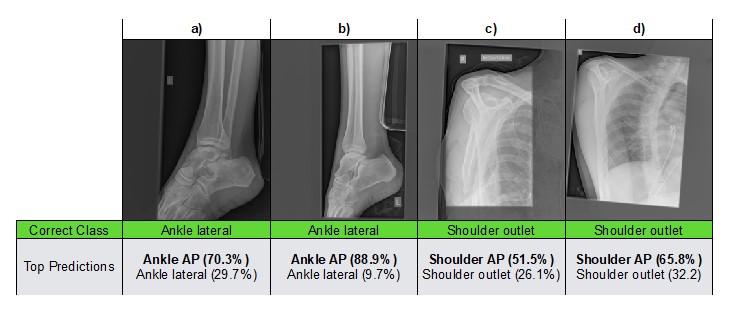
A deep learning algorithm for VHD diagnosis and evaluation
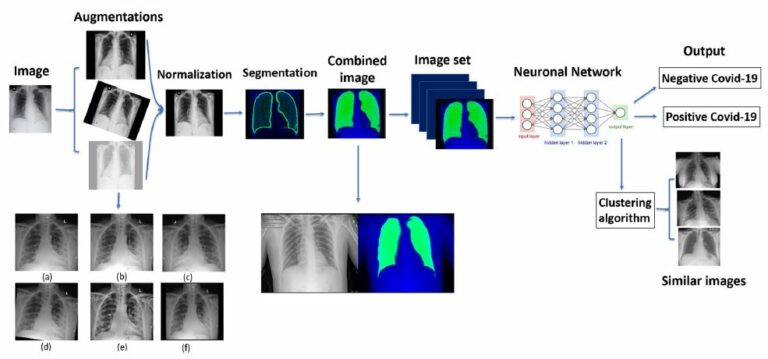
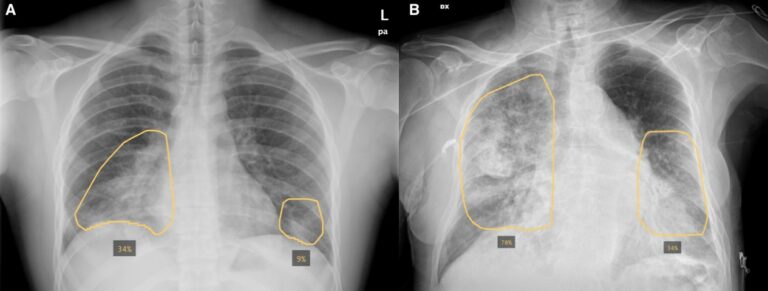
This study aims to develop and validate a deep learning-based automatic chest radiograph (CXR) cardiovascular border (CB) analysis algorithm (CB_auto) in order to diagnose and quantitatively evaluate valvular heart disease (VHD). The authors found that the CB_auto system, in coordination with the deep learning algorithm, provided highly reliable CB measurements, which, in turn, can be useful, not long daily clinical