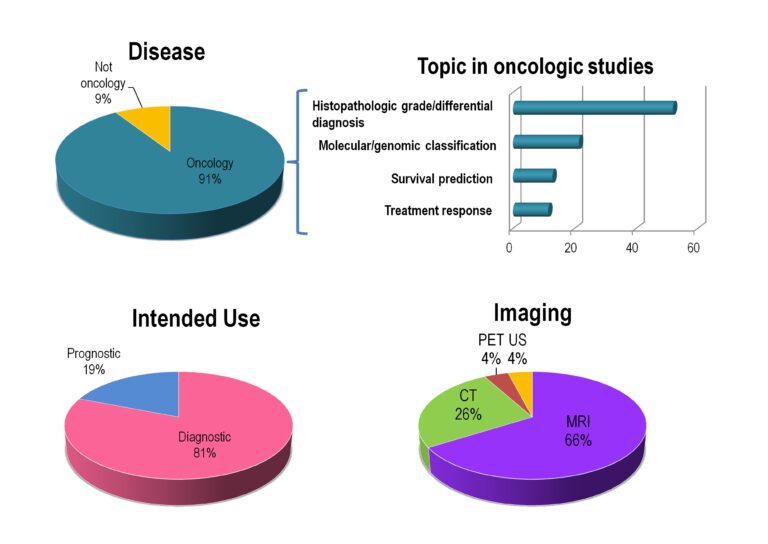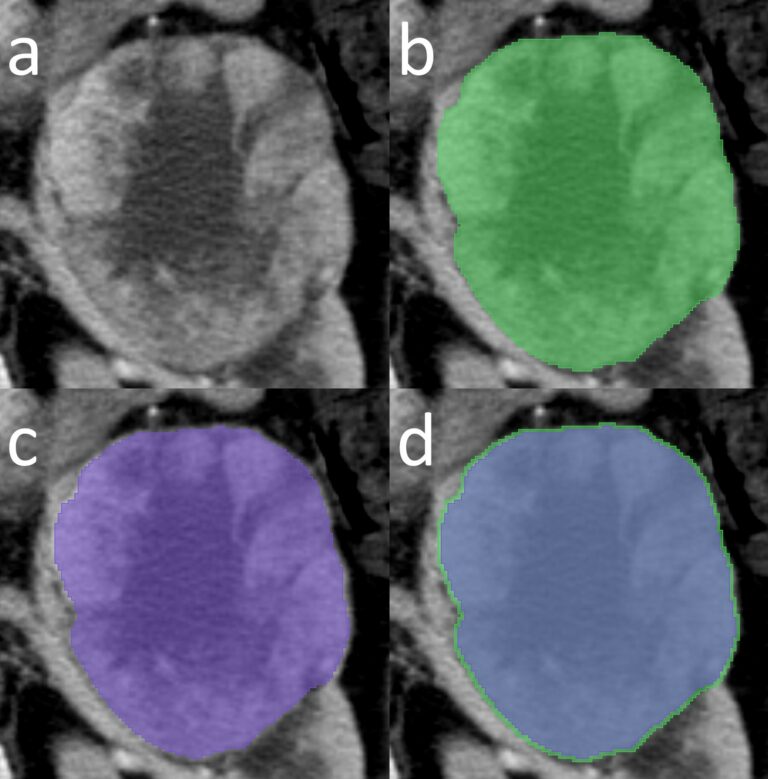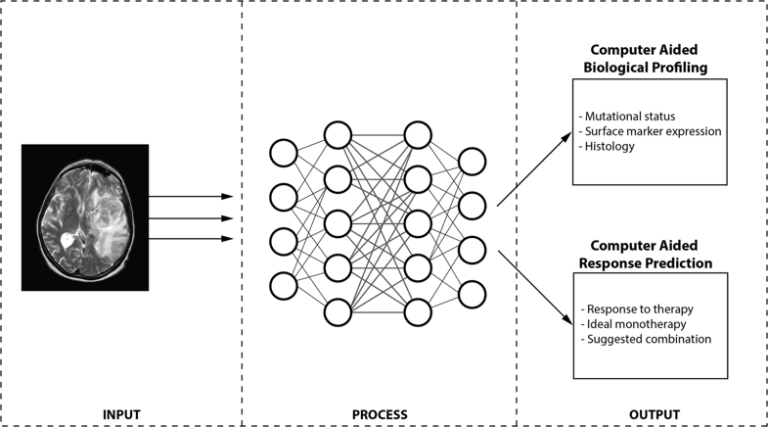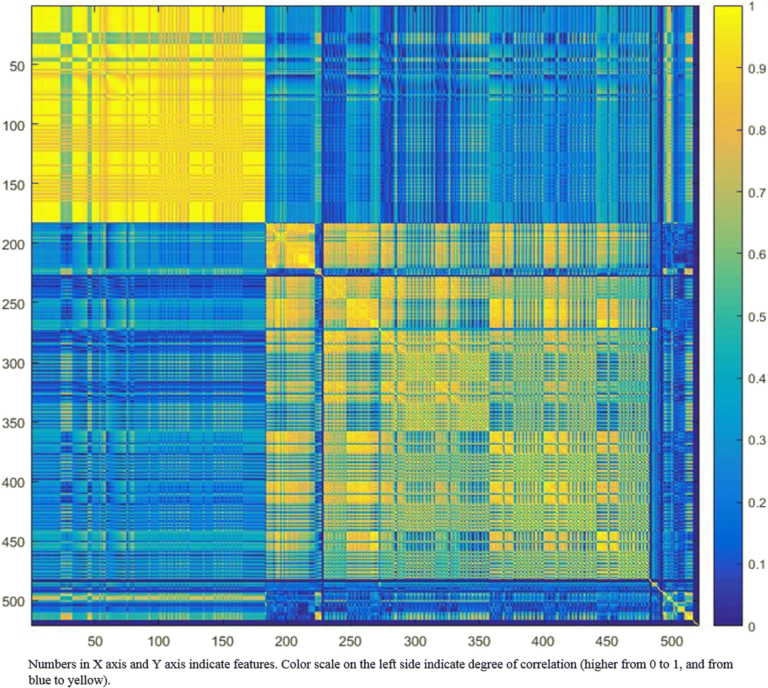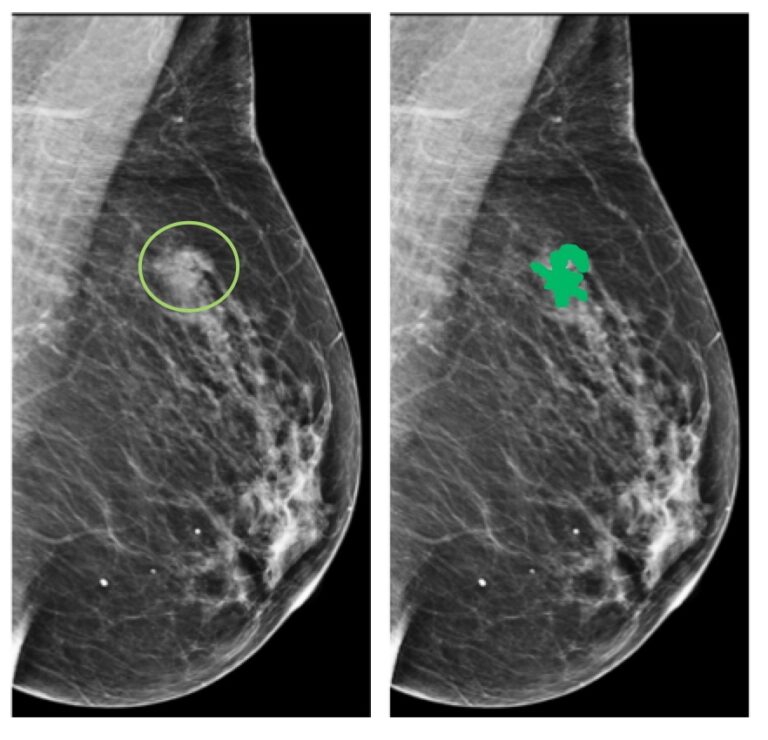
Breast cancer Ki-67 expression prediction by digital breast tomosynthesis radiomics features
Despite the encouraging results, more studies are needed in order to further evaluate these preliminary findings and to find to what extent radiomics and AI approaches can be integrated in clinical practice in a useful and reliable strategy [1]. I think that several issues reduce the application of radiomics approaches in clinical practice: the lack of knowledge of its basic