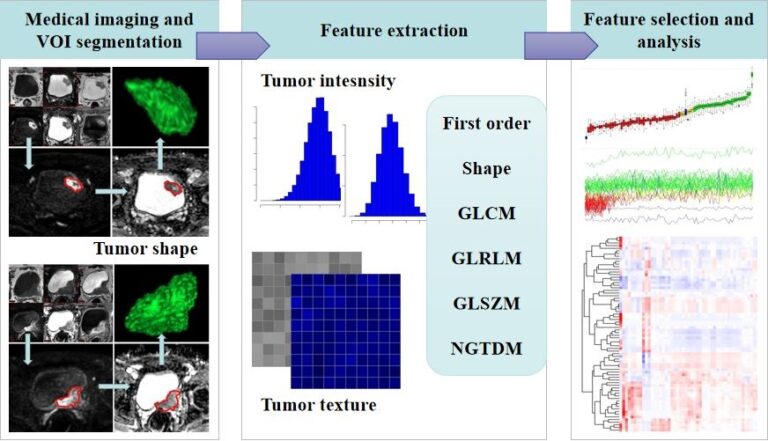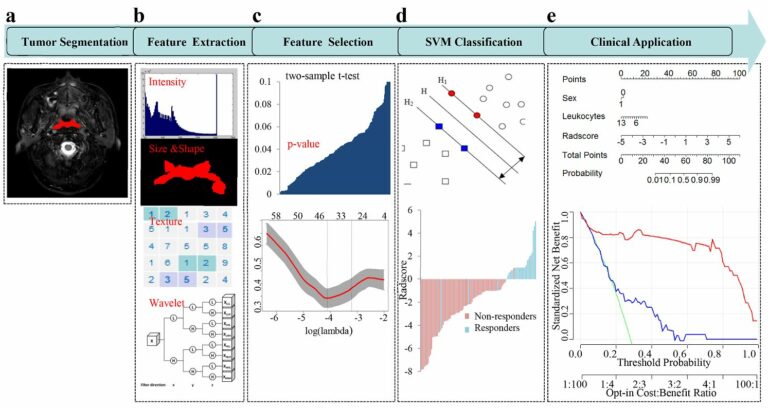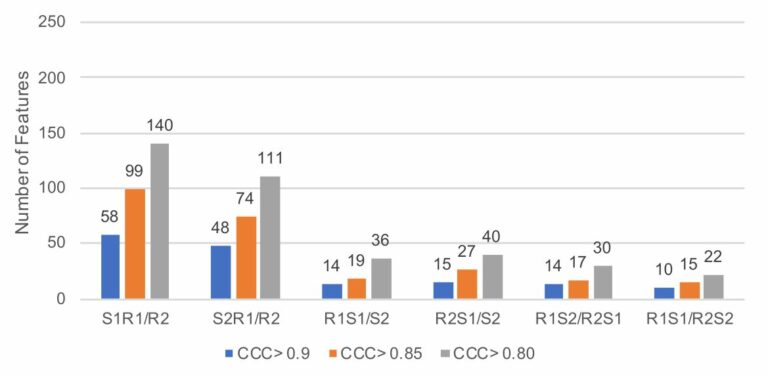
CT-based radiomics and machine learning to predict spread through air space in lung adenocarcinoma
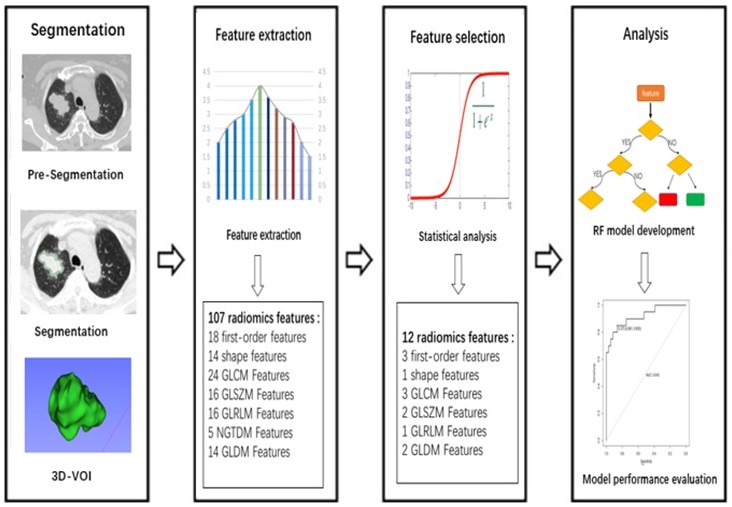
The authors of this retrospective study aimed to develop and validate a CT-based radiomics model for preoperative prediction of spread through air space (STAS) in lung adenocarcinoma. They found that a CT-based radiomics model can preoperatively predict, with good diagnosis performance, STAS in lung adenocarcinoma. Key points CT-based radiomics and machine learning model can predict spread through air space (STAS)