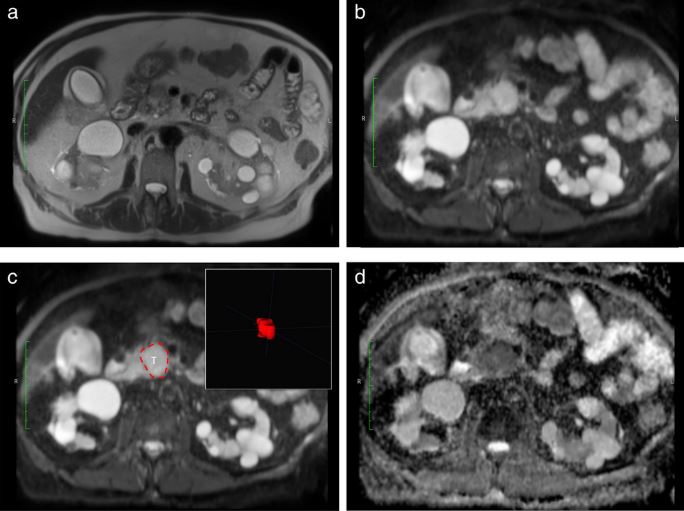
The aim of this study was to develop a supervised machine learning (ML) algorithm that would use diffusion-weighted imaging-derived radiomic features to predict median overall survival in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Based on the evaluation of 132 patients, it was determined that the use of ML allowed the prediction of overall survival with high diagnostic accuracy.
Key points
- Pancreatic cancer is a morphologically and genetically heterogeneous tumor entity.
- Histopathological subtypes of pancreatic cancer display different therapy response and survival.
- Whole-tumor radiomic analyses can capture and assess heterogeneity and its impact.
- This study applies machine learning to radiomic features derived from diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
- The algorithm developed allowed the prediction of overall survival and tumor subtype with high diagnostic accuracy in an independent validation cohort.
Authors: Georgios Kaissis, Sebastian Ziegelmayer, Fabian Lohöfer, Hana Algül, Matthias Eiber, Wilko Weichert, Roland Schmid, Helmut Friess, Ernst Rummeny, Donna Ankerst, Jens Siveke & Rickmer Braren