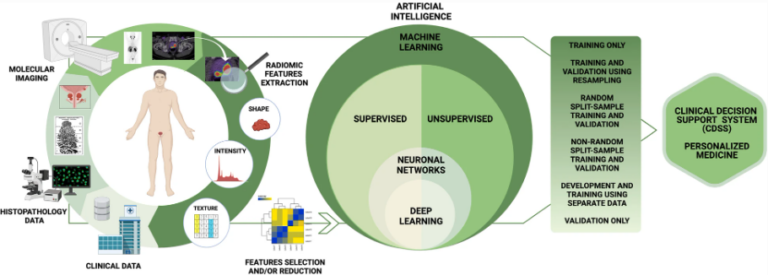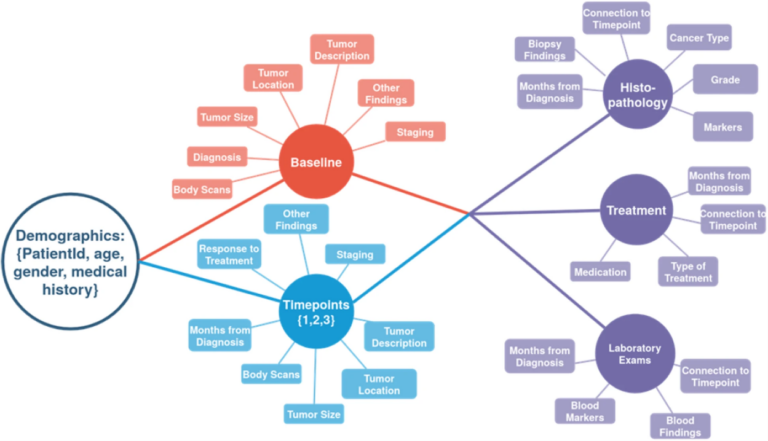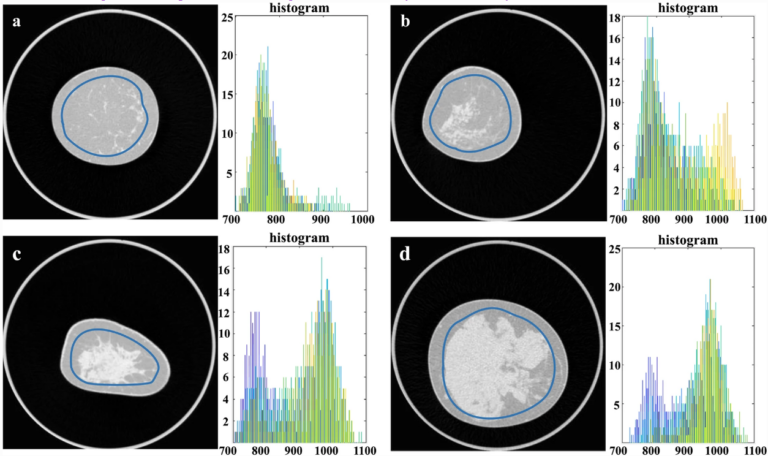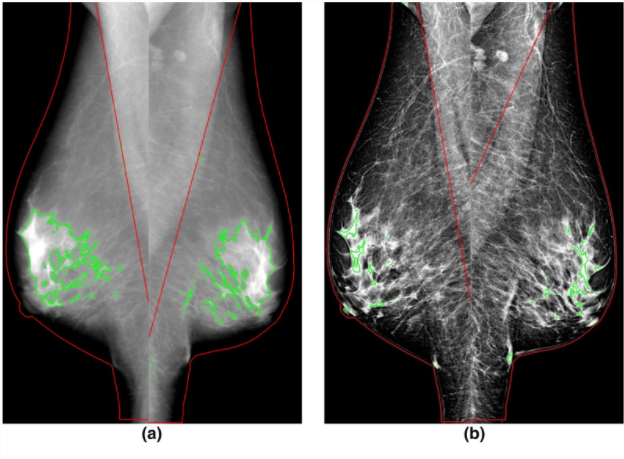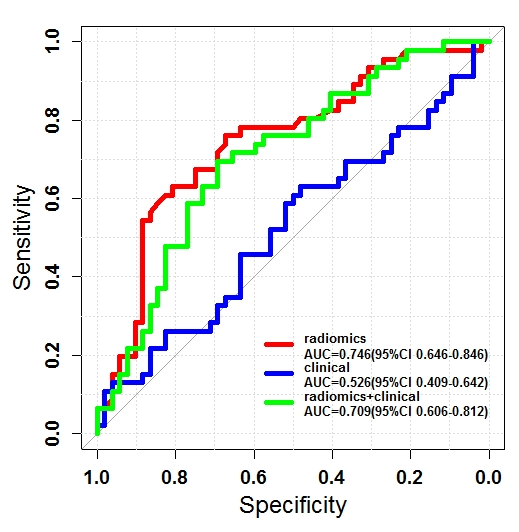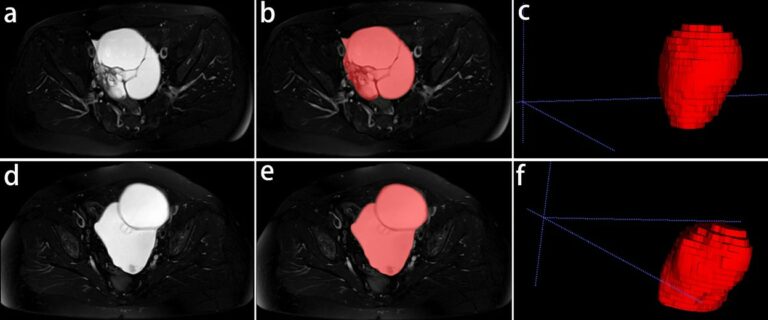
T2-weighted MRI-based radiomics discriminati between benign and borderline epithelial ovarian tumors
The authors of this study investigated whether radiomics based on T2-weighted MRI was able to discriminate between benign and borderline epithelial ovarian tumors (EOTs) preoperatively. They were able to show that it can provide critical diagnostic information in the discrimination between benign and borderline EOTs, showing that there is potential to aid personalized treatment options. Key points T2-weighted MRI-based radiomics