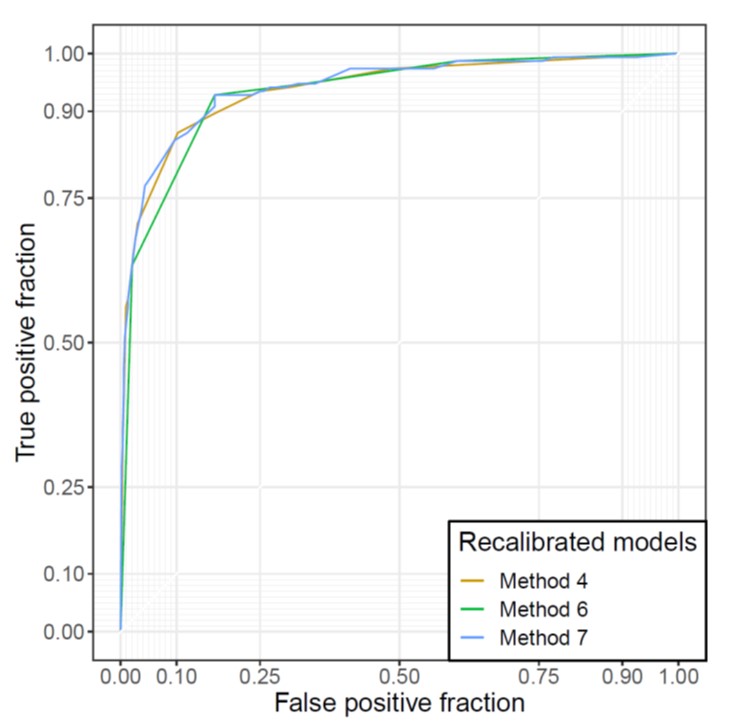
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the calibration of a deep learning (DL) model in a diagnostic cohort, as well as to improve the model’s calibration through recalibration procedures. The authors found that the calibration of the DL algorithm can be augmented through simple recalibration procedures, and improved calibration may enhance the interpretability and credibility of the model for users.
Key points
- A deep learning model tended to overestimate the likelihood of the presence of abnormalities in chest radiographs.
- Simple recalibration of the deep learning model using output scores could improve the calibration of model while maintaining discrimination.
- Improved calibration of a deep learning model may enhance the interpretability and the credibility of the model for users.
Authors: Eui Jin Hwang, Hyungjin Kim, Jong Hyuk Lee, Jin Mo Goo & Chang Min Park