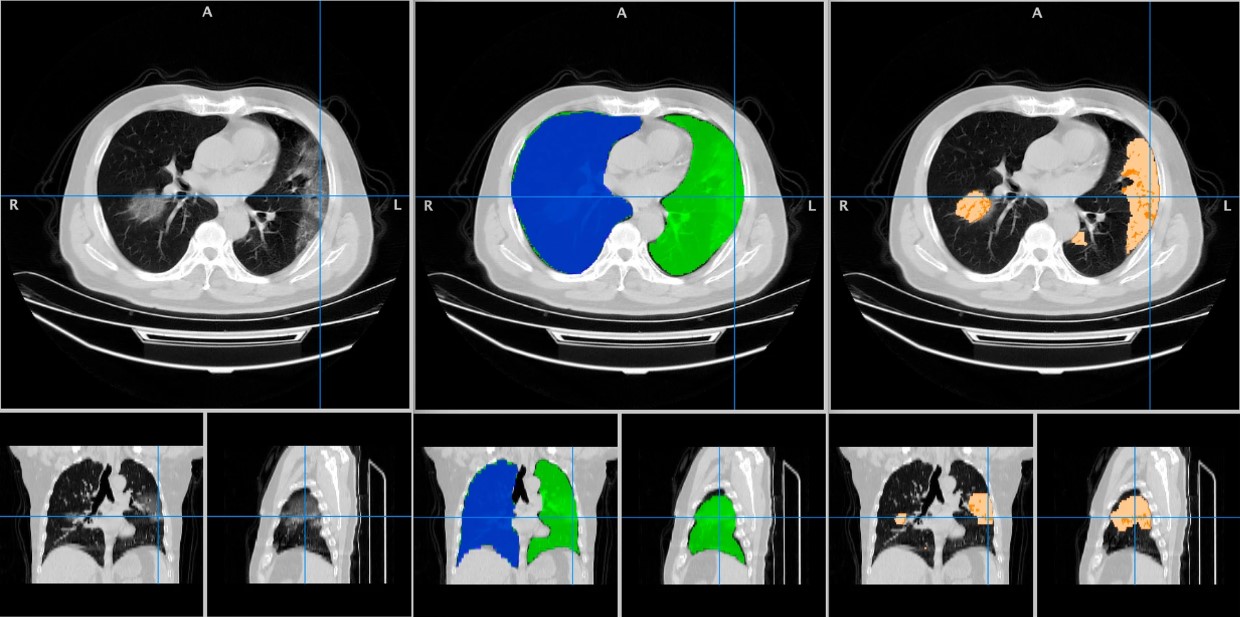
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of the LungQuant system, which is a deep learning-based software for quantitative analysis of chest CT. LungQuant was evaluated by comparing its results with independent visual evaluations by a group of clinical experts. The results indicated that an automatic quantification tool may be beneficial and contribute to an improved clinical workflow of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Key points
- We conducted a multicenter evaluation of the deep learning-based LungQuant automated software.
- We translated qualitative assessments into quantifiable metrics to characterize coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia lesions.
- Comparing the software output to the clinical evaluations, results were satisfactory despite heterogeneity of the clinical evaluations.
- An automatic quantification tool may contribute to improve the clinical workflow of COVID-19 pneumonia.
Authors: Camilla Scapicchio, Andrea Chincarini, Elena Ballante, Luca Berta, Eleonora Bicci, Chandra Bortolotto, Francesca Brero, Raffaella Fiamma Cabini, Giuseppe Cristofalo, Salvatore Claudio Fanni, Maria Evelina Fantacci, Silvia Figini, Massimo Galia, Pietro Gemma, Emanuele Grassedonio, Alessandro Lascialfari, Cristina Lenardi, Alice Lionetti, Francesca Lizzi, Maurizio Marrale, Massimo Midiri, Cosimo Nardi, Piernicola Oliva, Noemi Perillo, Ian Postuma, Lorenzo Preda, Vieri Rastrelli, Francesco Rizzetto, Nicola Spina, Cinzia Talamonti, Alberto Torresin, Angelo Vanzulli, Federica Volpi, Emanuele Neri & Alessandra Retico