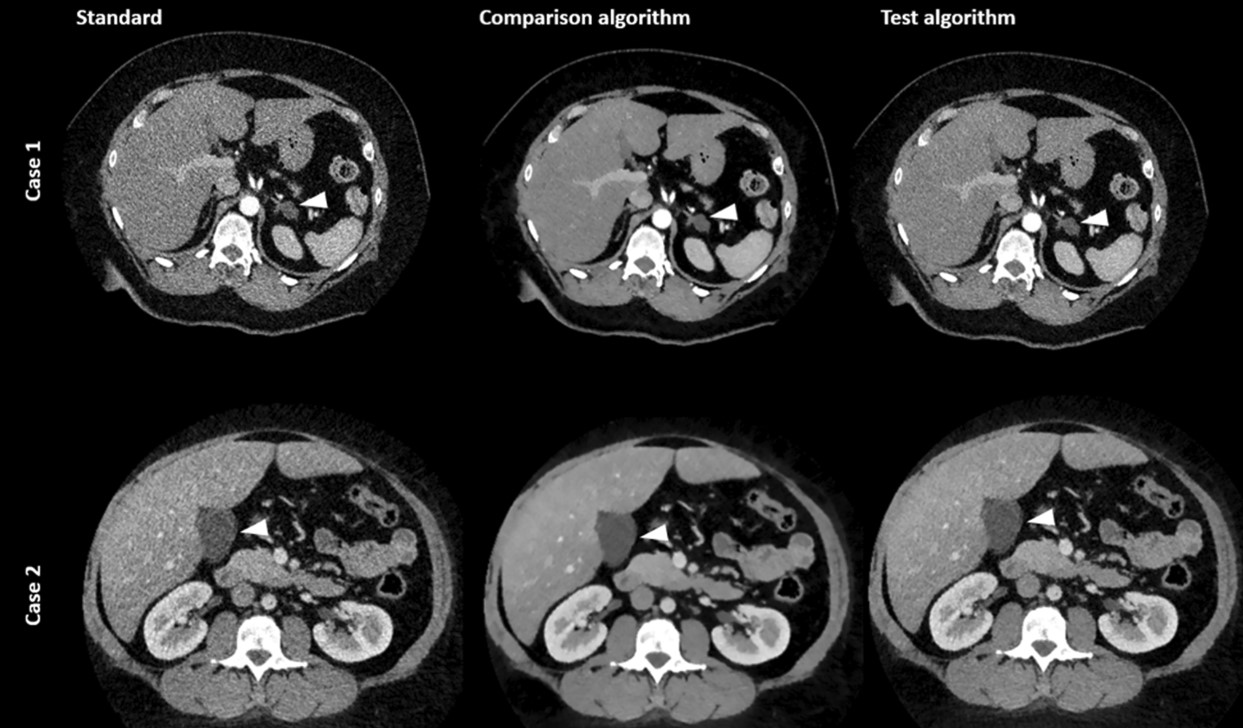
In the ever-evolving landscape of radiology, the quest for enhanced image quality and reduced noise, particularly in obese patients, remains an enduring challenge. It is within this context that a novel algorithm for noise reduction in dual-source dual-energy (DE) CT imaging is a promising development.
In a retrospective study involving seventy-nine patients with contrast-enhanced abdominal imaging, this novel algorithm was put to the test. The patients, representing a cohort with a BMI ranging from 35 to 62 kg/m2, underwent imaging with dual-energy CT scanners.
One of our primary findings was the substantial increase in the contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) achieved through the application of the test algorithm. In addition, four blinded readers who assessed the images for perceived image noise, quality, and diagnostic comfort agreed on perceived image noise and overall quality, which underscores the reliability of the new algorithm in producing images that meet or exceed the standards set by existing denoising techniques.
In an era where patient-centric care and precision medicine are at the forefront of healthcare, any advancement that improves the diagnostic capabilities of imaging technology is of high clinical relevance. The potential of this novel algorithm to enhance the diagnostic process for obese patients imaged with DECT opens new avenues for better patient care and clinical reads.
While this study offers a glimpse into the capabilities of this new denoising algorithm, our group is planning to perform further research and validation to ascertain its broader applicability and impact across diverse clinical scenarios.
Key points
- Improving image quality in DECT imaging of obese patients is important for accurate and confident clinical reads, which may be aided by novel denoising algorithms using image domain data.
- Accurate diagnosis on CT imaging of obese patients is especially challenging and denoising algorithms can increase quantitative and qualitative image quality.
- Image domain algorithms can generalize well and can be implemented at other institutions.
Authors: Fides R. Schwartz, Darin P. Clark, Francesca Rigiroli, Kevin Kalisz, Benjamin Wildman-Tobriner, Sarah Thomas, Joshua Wilson, Cristian T. Badea & Daniele Marin