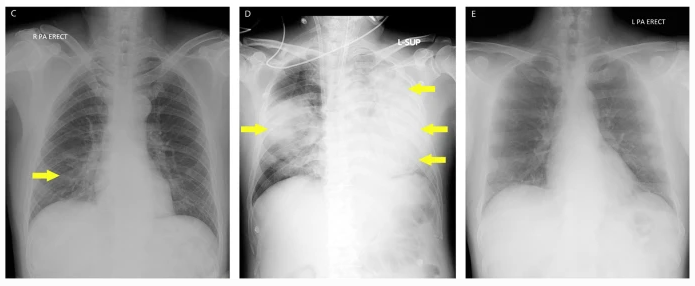
Due to the challenges associated with differentiating COVID-19 from the number of respiratory infections that can appear on chest radiographs (CXR), the authors of this study developed and validated an AI system for COVID-19 detection on presenting CXR. This was achieved by training a deep learning model on nearly 170,000 CXRs, and was subsequently validated on a large international test set of presenting CXRs of symptomatic patients across 9 study sites and 2 public datasets. This study provides a set of realistic expectations which could be useful for studying and gauging radiological AI model performance.
Key points
- An AI model developed using CXRs to detect COVID-19 was validated in a large multi-center cohort of 5,894 patients from 9 prospectively recruited sites and 2 public datasets.
- Differences in AI model performance were seen across region, disease severity, gender, and age.
- Prevalence simulations on the international test set demonstrate the model’s NPV is greater than 98.5% at any prevalence below 4.5%.
Authors: Michael D. Kuo, Keith W. H. Chiu, David S. Wang, Anna Rita Larici, Dmytro Poplavskiy, Adele Valentini, Alessandro Napoli, Andrea Borghesi, Guido Ligabue, Xin Hao B. Fang, Hing Ki C. Wong, Sailong Zhang, John R. Hunter, Abeer Mousa, Amato Infante, Lorenzo Elia, Salvatore Golemi, Leung Ho P. Yu, Christopher K. M. Hui & Bradley J. Erickson