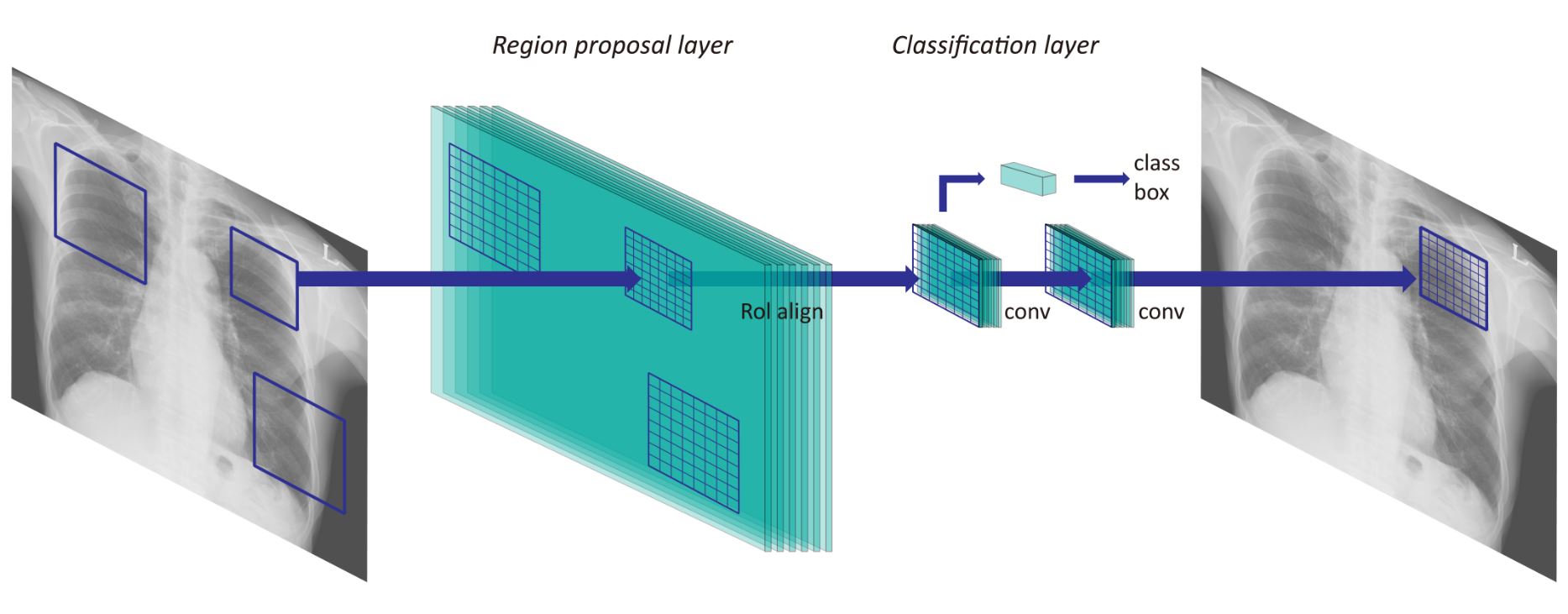
In this study, the authors retrospectively collected 2,088 abnormal and 352 normal chest radiographs from two institutions in order to investigate the optimal input matrix size for deep learning-based computer-aided detection (CAD) of nodules and masses on chest radiographs. This resulted in the matrix size 896 as having the highest performance for various sizes of abnormalities using different convolutional neural networks, which could improve CAD performance without having to use additional training data.
Key points
- Input matrix size significantly affected the performance of a deep learning-based CAD for detection of nodules or masses on chest radiographs.
- The matrix size 896 showed the best performance in two different CNN detection models.
- The optimal matrix size of chest radiographs could enhance CAD performance without additional training data.
Authors: Young-Gon Kim, Sang Min Lee, Kyung Hee Lee, Ryoungwoo Jang, Joon Beom Seo & Namkug Kim