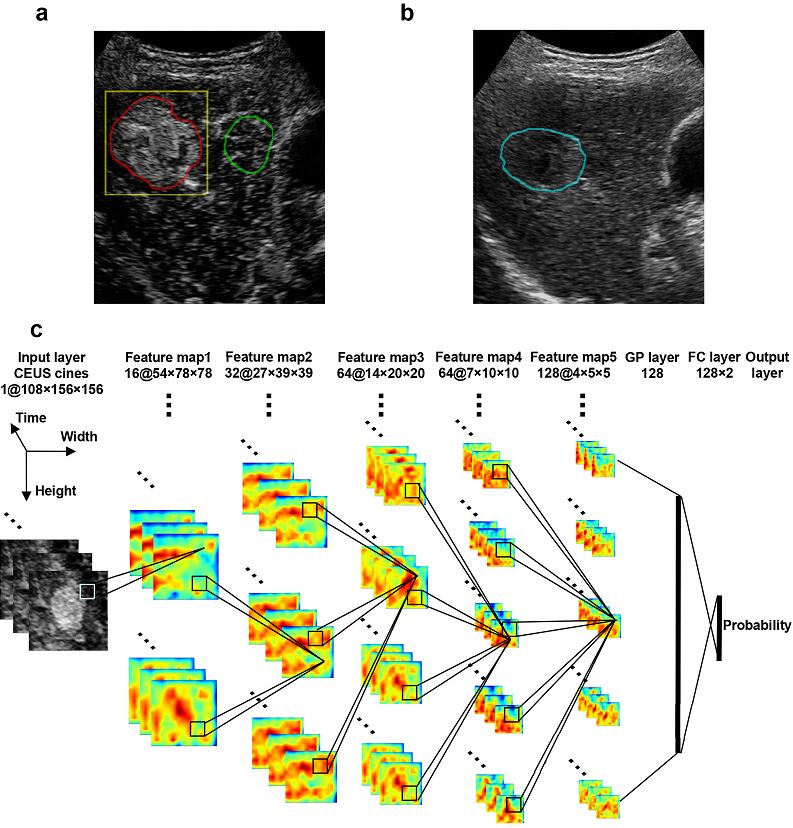
The aim of this study was to establish and validate an artificial intelligence-based radiomics strategy in order to predict personalized responses to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to first transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) by analyzing contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) cines quantitatively. This was done using 130 HCC patients, showing that a deep learning-based radiomics method can effectively utilize CEUS, resulting in accurate and personalized prediction.
Key points
- Deep learning (DL) radiomics-based CEUS model can accurately predict responses of HCC patients to their first TACE session by quantitatively analyzing their pre-operative CEUS cines.
- The visualization of the 3D CNN analysis adopted in CEUS model provided direct insight into what computers “see” on CEUS cines, which can help people understand the interpretation of CEUS data.
- The proposed prediction method is easy to operate and labor-saving for clinical practice, facilitating the clinical treatment decision of HCCs with very few time costs.
Authors: Dan Liu, Fei Liu, Xiaoyan Xie, Liya Su, Ming Liu, Xiaohua Xie, Ming Kuang, Guangliang Huang, Yuqi Wang, Hui Zhou, Kun Wang, Manxia Lin & Jie Tian