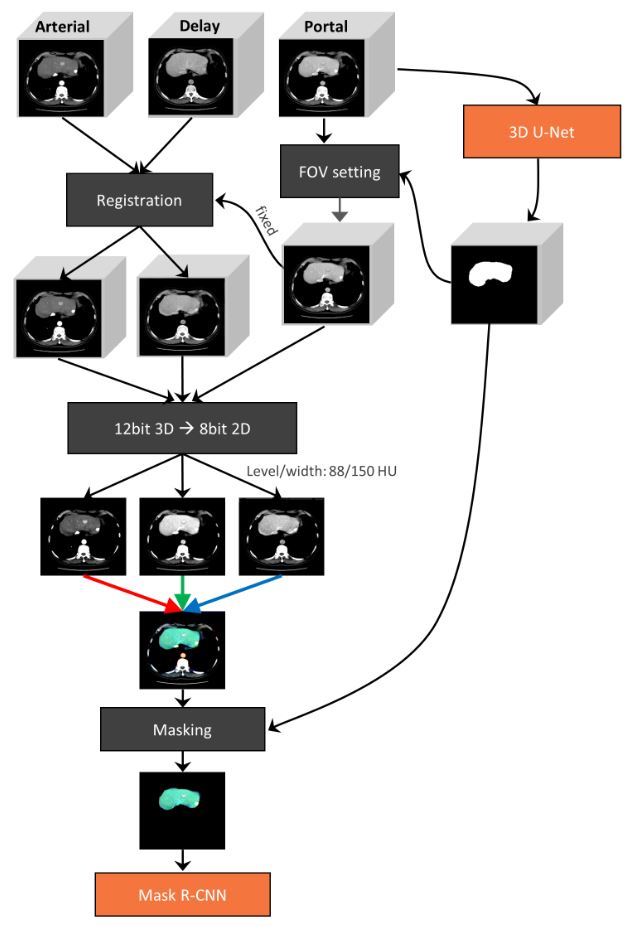
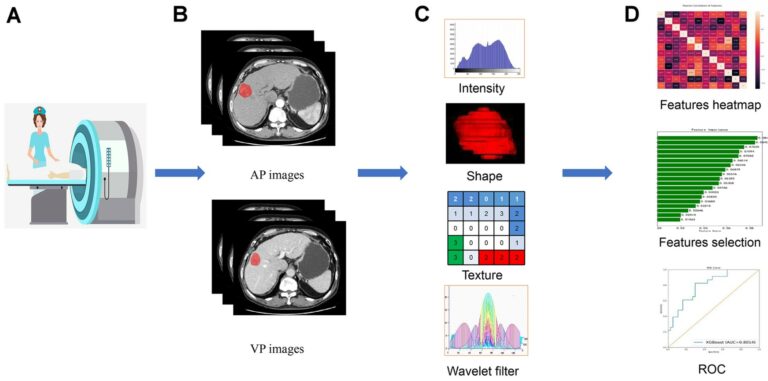
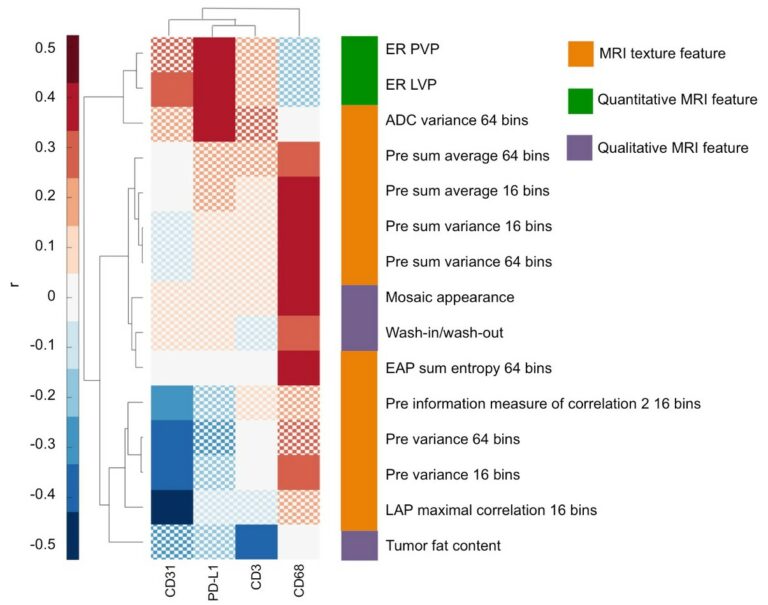
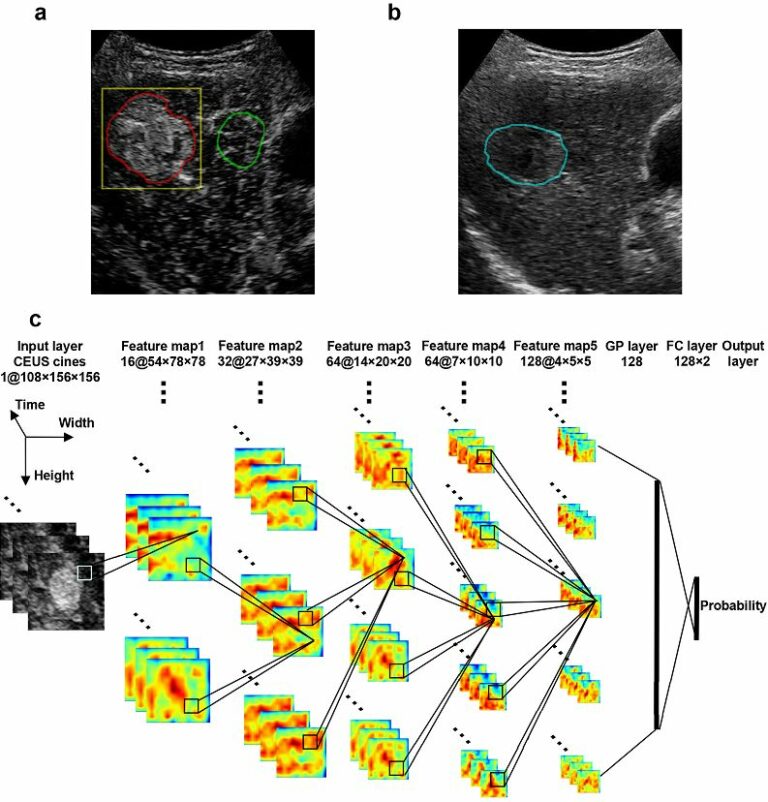
Precision of MRI radiomics features in the liver and HCC
The aim of this study, consisting of a population of 55 patients who underwent two repeat contrast-enhanced abdominal MRI exams within 1 month, was to assess the precision of MRI radiomics features in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumors and liver parenchyma. The authors determined that MRI radiomics features have acceptable repeatability in the liver and HCC when using the same MRI