Multiple automated methods for segmentation of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions have been developed over the past years, and the use of artificial neural networks (ANN) has recently generated many outstanding results in the public segmentation challenges. As we all know from our work as radiologists, the routine clinical practice is always conducted with an economical balance between optimal scan times and good image quality, and in this context dealing with image artifacts is part of the daily routine. Therefore, a truly clinically-applicable method also needs to be able to deal with the image quality coming from an unselected cohort of routine scans.
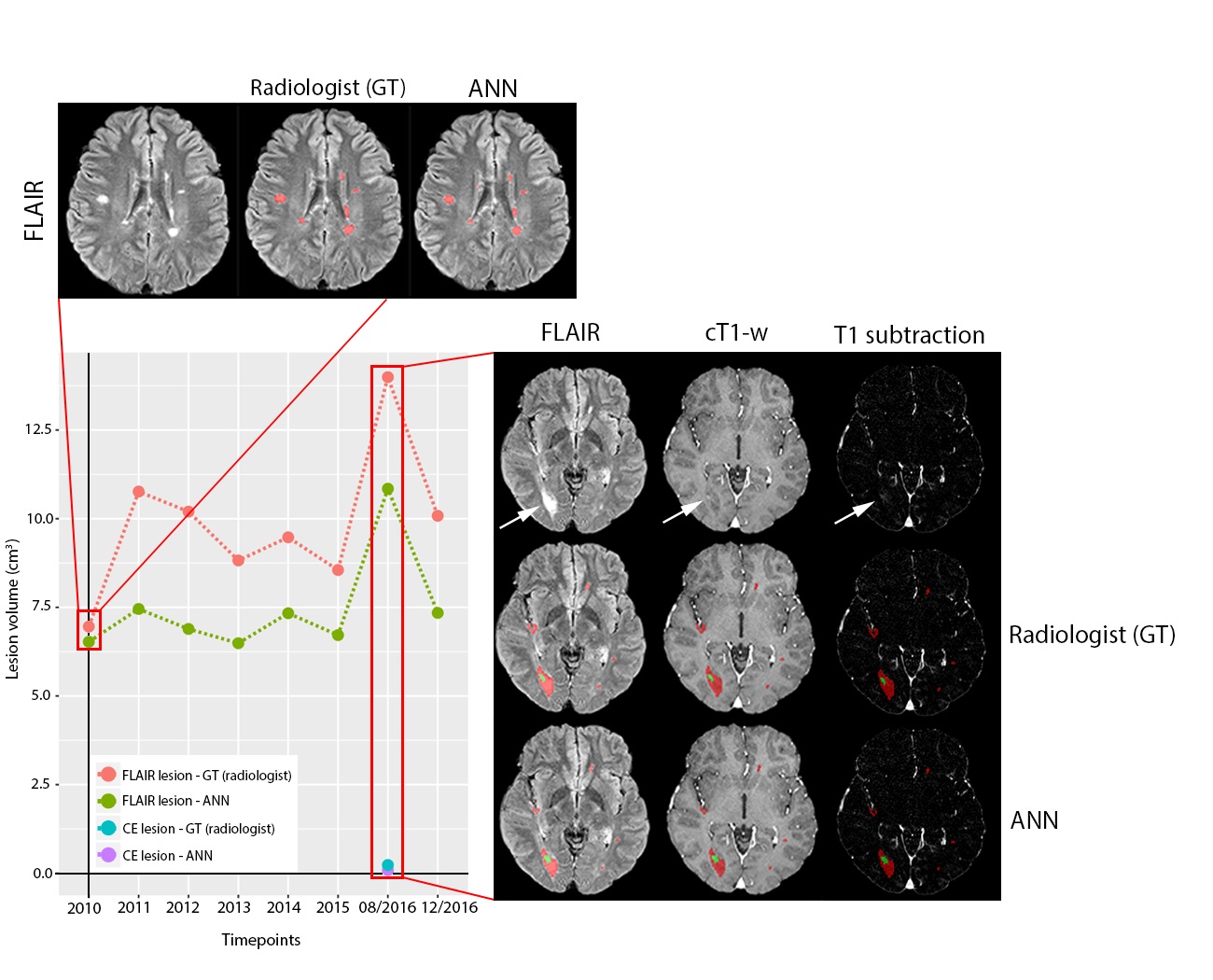
In our work we tried to prove that a well-trained ANN can indeed perform well, also when facing unselected data from the clinical routine. We based our ANN on the popular U-NET architecture, and we selected a large cohort of MS patients with longitudinal scans obtained at our institution, (1) without excluding data with “suboptimal” quality, meaning that we included scans with some artifacts (which would still be used for reporting in a routine setting), as well as (2) including all possible disease forms, ranging from new diagnoses with very few lesions to terminal patients with very high lesion volume, as well as active lesions (presenting contrast enhancements).
We show that the ANN was capable to accurately segment both T2/FLAIR-hyperintense and contrast-enhancing (CE) lesions. Moreover, the network presents two striking advantages as compared to a human rater: first, it is able to fully segment and assess disease status within some seconds, as compared to the lengthy and labor-intensive human segmentation; second, it presents intrinsic reproducibility and consistency, meaning that it applies the same criteria for all the evaluated exams and is not influenced by the intra- and/or inter-observer variability of human work. Overall, our results highlight the capability of ANN for quantitative state-of-the-art assessment of volumetric lesion load on MRI and potentially enable a more accurate assessment of disease burden in patients with MS.
Key points
- Artificial neural networks (ANN) can accurately detect and segment both T2/FLAIR and contrast-enhancing MS lesions in MRI data.
- Performance of the ANN was consistent in a clinically derived dataset, with patients presenting all possible disease stages in MRI scans acquired from standard clinical routine rather than with high-quality research sequences.
- Computer-aided evaluation of MS with ANN could streamline both clinical and research procedures in the volumetric assessment of MS disease burden as well as in lesion detection.
Authors: Gianluca Brugnara, Fabian Isensee, Ulf Neuberger, David Bonekamp, Jens Petersen, Ricarda Diem, Brigitte Wildemann, Sabine Heiland, Wolfgang Wick, Martin Bendszus, Klaus Maier-Hein & Philipp Kickingereder