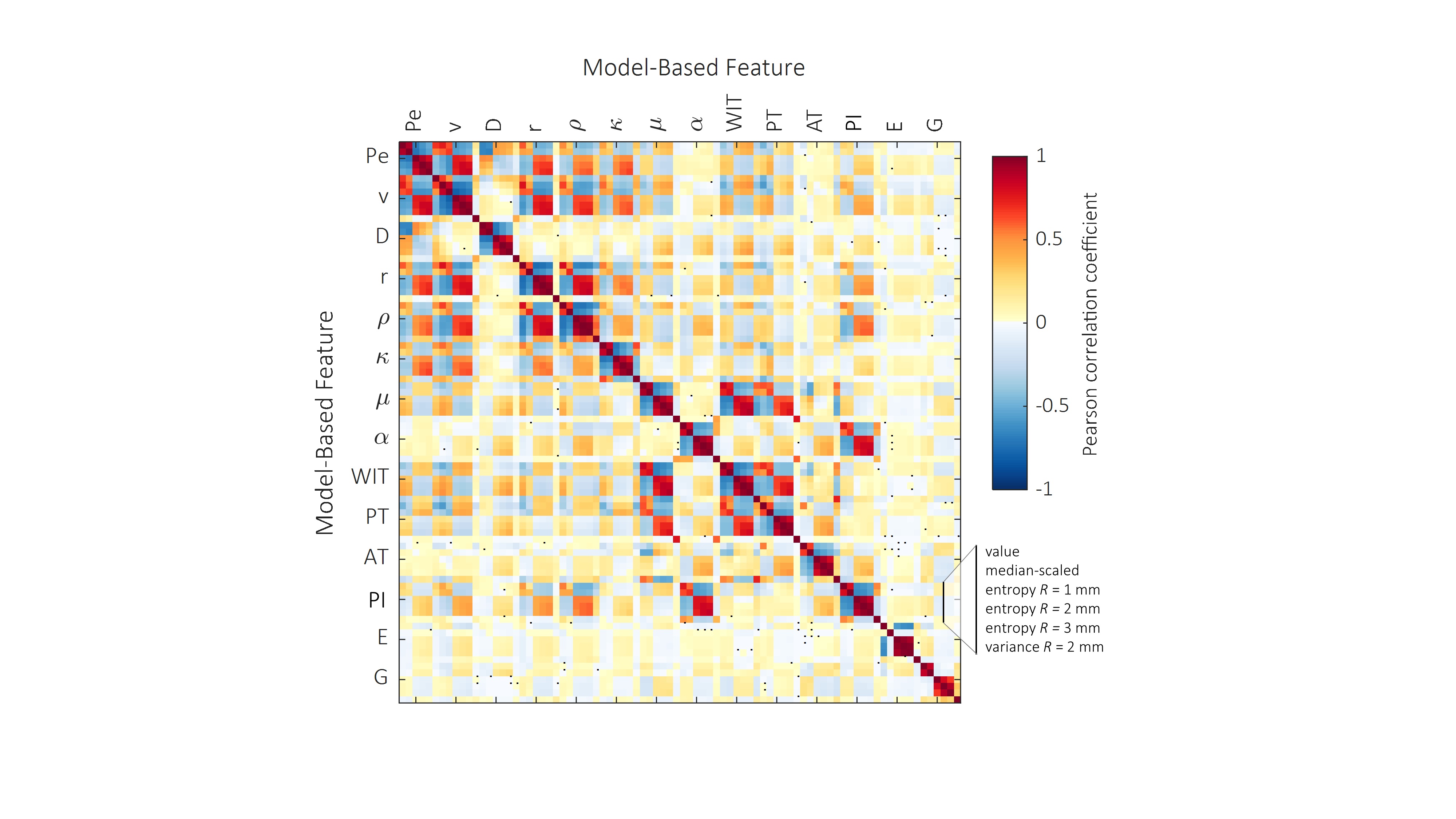
In this study, the authors aimed to assess the potential of machine learning (ML) based on B-mode, shear-wave elastography (SWE), and dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasound (DCE-US) radiomics for the localization of prostate cancer lesions using transrectal ultrasound. The authors were able to demonstrate the technical feasibility of multiparametric ML to improve upon single US modalities for the localization of prostate cancer.
Key points
- Combination of B-mode ultrasound, shear-wave elastography, and contrast ultrasound radiomics through machine learning is technically feasible.
- Multiparametric ultrasound demonstrated a higher prostate cancer localization ability than single ultrasound modalities.
- Computer-aided multiparametric ultrasound could help clinicians in biopsy targeting.
Authors: Rogier R. Wildeboer, Christophe K. Mannaerts, Ruud J. G. van Sloun, Lars Budäus, Derya Tilki, Hessel Wijkstra, Georg Salomon, Massimo Mischi