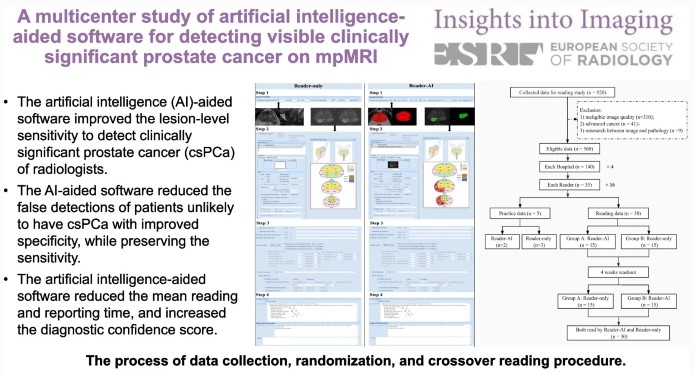
This study seeks to determine if artificial intelligence (AI)-based software can improve radiologists’ performance when detecting clinically significant prostate cancer. Sixteen radiologists from four hospitals participated and were assigned 30 cases, half without AI and half with AI. The authors determined that the AI software improves the performance of radiologists by reducing false positive detection of prostate cancer patients while also improving reading times and diagnostic confidence.
Key points
- The artificial intelligence (AI)-aided software improved the lesion-level sensitivity to detect MRI- visible clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) of radiologists.
- The AI-aided software reduced the false positive detection of prostate cancer patients with improved specificity while preserving the sensitivity.
- The AI-aided software reduced the mean reading and reporting time and increased the diagnostic confidence score for MRI-visible csPCa diagnosis.
Authors: Zhaonan Sun, Kexin Wang, Zixuan Kong, Zhangli Xing, Yuntian Chen, Ning Luo, Yang Yu, Bin Song, Pengsheng Wu, Xiangpeng Wang, Xiaodong Zhang & Xiaoying Wang