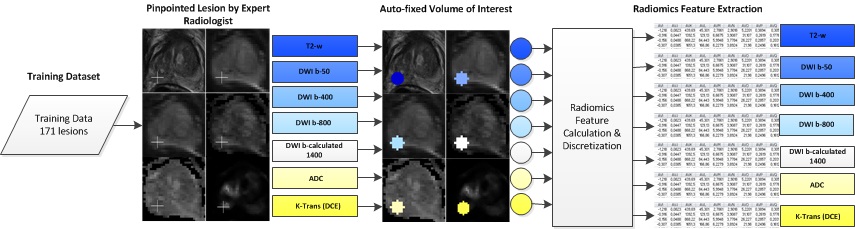
The purpose of this study was to create a radiomics approach based on multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) features that were extracted from an auto-fixed volume of interest (VOI) that quantifies the phenotype of clinically significant peripheral zone prostate cancer (pCA). The study included 206 patients and the authors concluded that the developed radiomics model that extracts mpMRI features with an auto-fixed VOI may be a valuable addition to visual assessment in diagnosing clinically significant pCA.
Key points
- T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging features are essential components of a radiomics model for clinically significant prostate cancer; addition of dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging does not significantly improve diagnostic performance.
- Multivariate feature selection and extreme gradient outperform univariate feature selection and random forest.
- The developed radiomics model that extracts multiparametric MRI features with an auto-fixed volume of interest may be a valuable addition to visual assessment in diagnosing clinically significant prostate cancer.
Authors: Jeroen Bleker, Thomas C. Kwee, Rudi A. J. O. Dierckx, Igle Jan de Jong, Henkjan Huisman, Derya Yakar