Prediction of lipomatous soft tissue malignancy on MRI
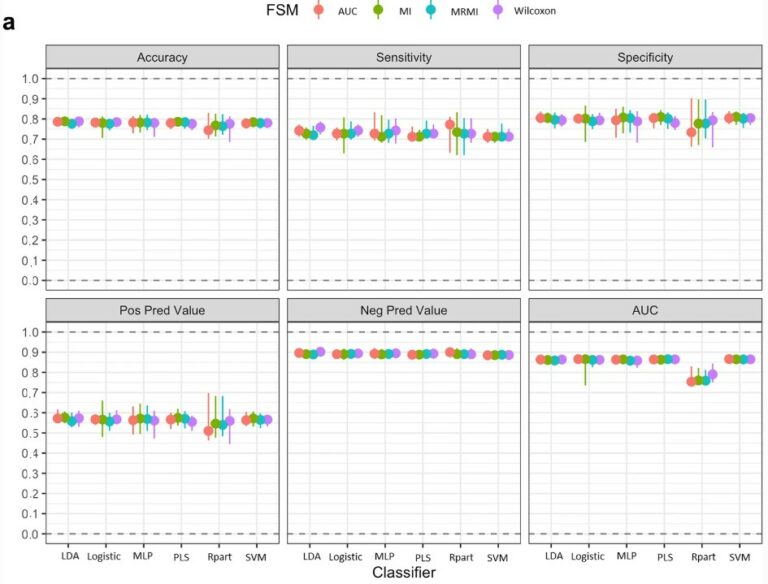
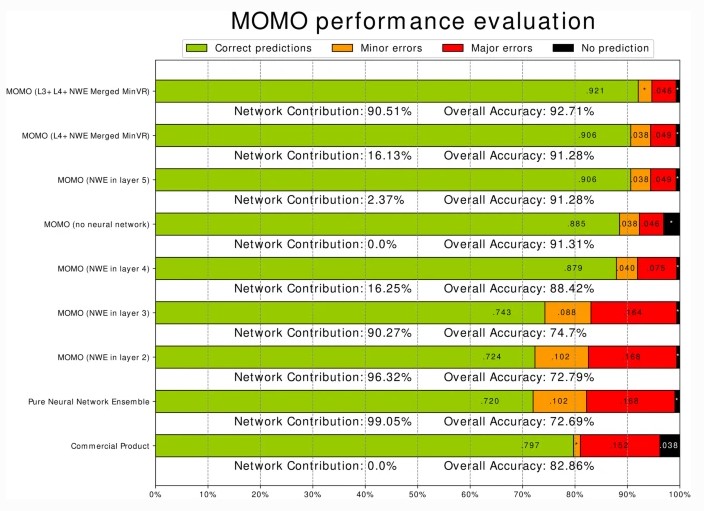
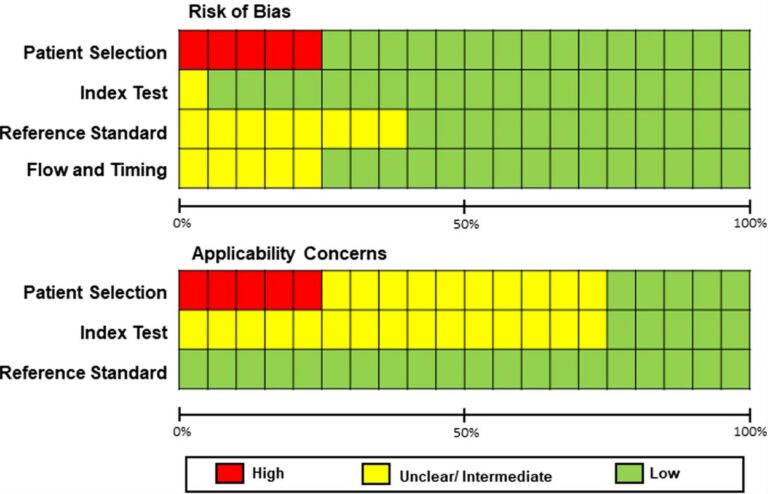
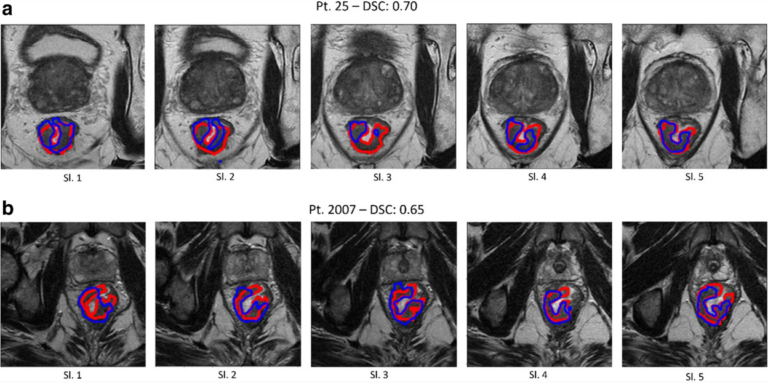
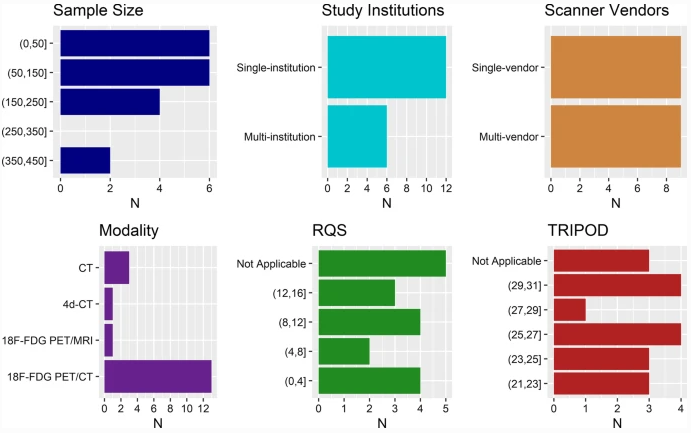
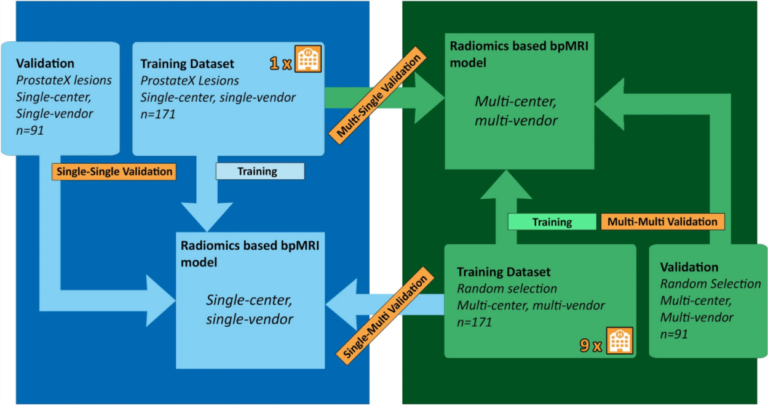
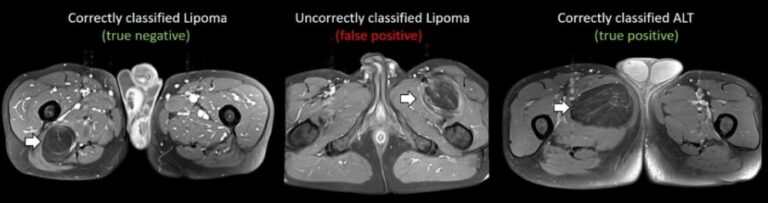
This study, which included a cohort of 145 patients affected by lipomatous soft tissue tumours, aimed to compare the performances of MRI radiomic machine learning analysis with that of deep learning in order to predict malignancy in patients with lipomas oratypical lipomatous tumours. The authors were able to show that batch-effect corrected machine learning and radiomics approaches outperformed deep learning-based