Prediction of pulmonary pressure after Glenn shunts by computed tomography–based machine learning models
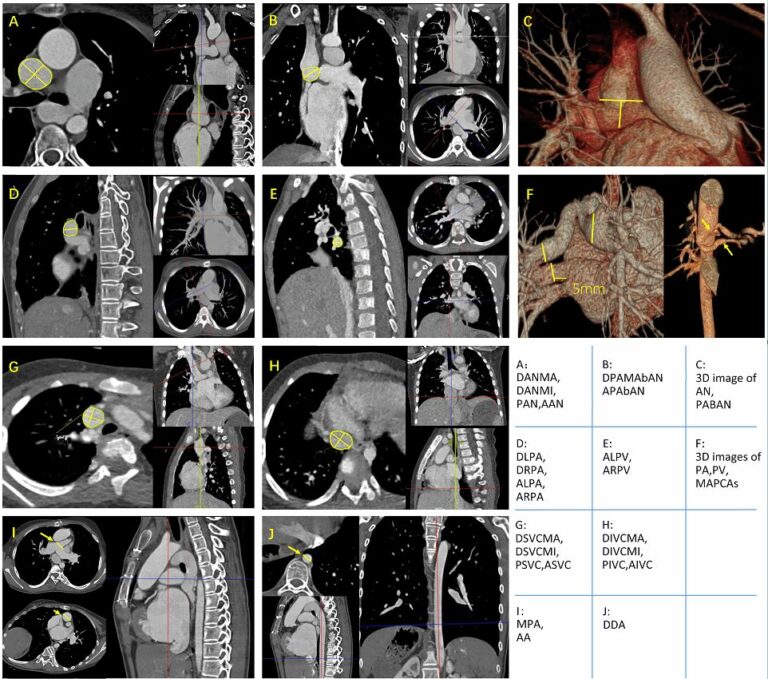
The aim of this retrospective study was to develop non-invasive machine learning (ML) classifiers for predicting post-Glenn shunt patients with low and high risks of a mean pulmonary arterial pressure above 15 mmHg, which was based on pre-operative cardiac CT. The study included 96 patients who underwent a bidirectional Glenn procedure. Key points Twenty-three candidate descriptors were manually extracted from









