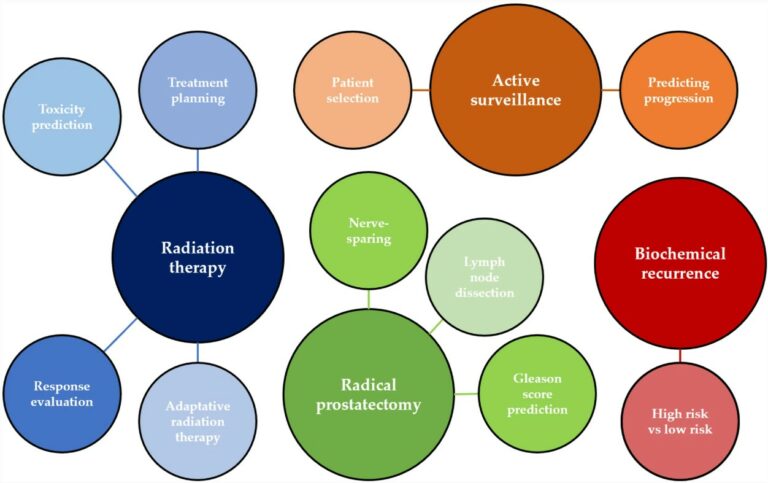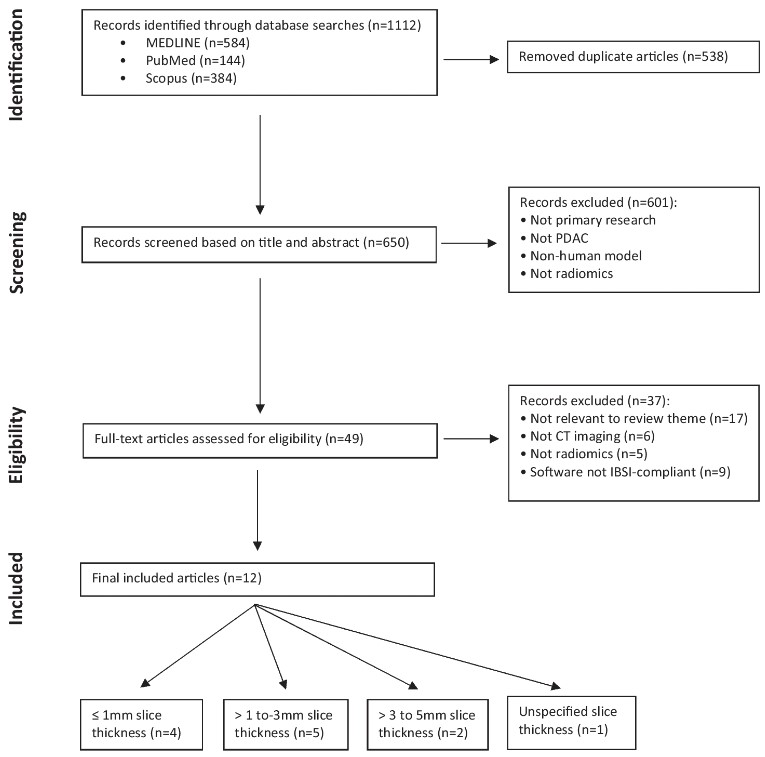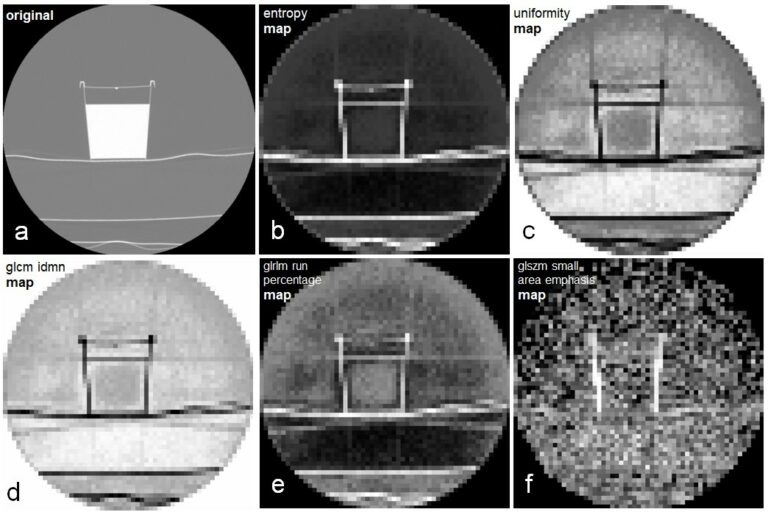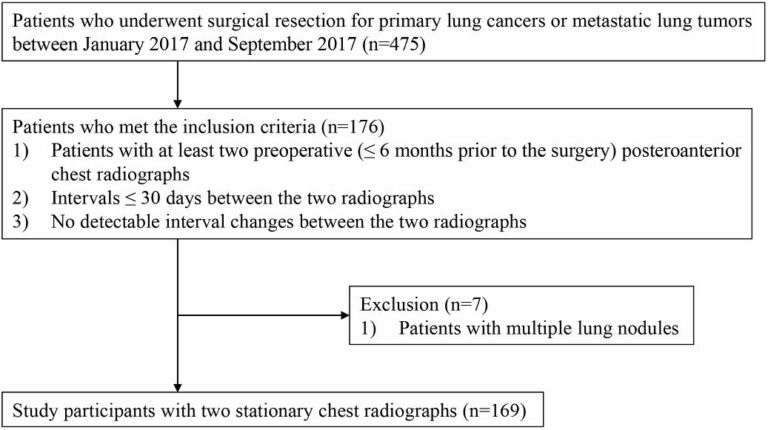
Reproducibility of radiomics quality score: an intra- and inter-rater reliability study
The rapidly evolving field of radiomics research holds the potential to revolutionize medicine by transforming diagnostic images into quantifiable data. Assessing the quality of radiomics research is challenging and requires reliable tools for standardization. Our results, published in European Radiology, have revealed some room for improvement regarding the reproducibility of the widely used Radiomics Quality Score (RQS). We recruited multiple