Radiomics in predicting treatment response in non-small-cell lung cancer: current status, challenges and future perspectives
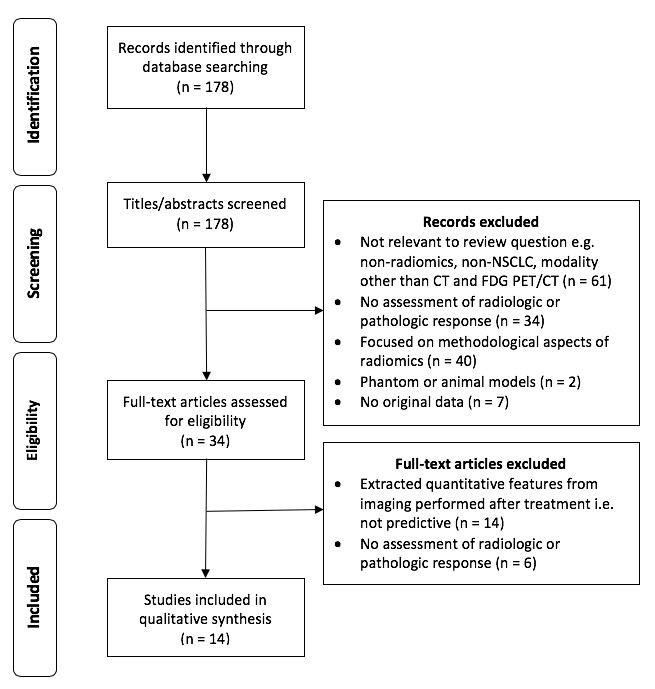
This literature review summarizes the current status and evaluates the scientific reporting quality of radiomics research in the prediction of treatment response in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The authors performed this literature review through a comprehensive literature search using the PubMed database, screening a total of 178 articles for eligibility. Key points The included studies reported several promising radiomic markers