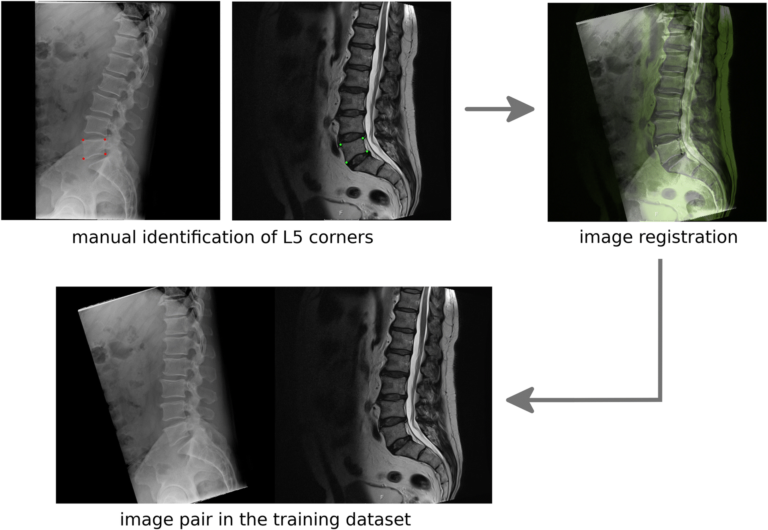
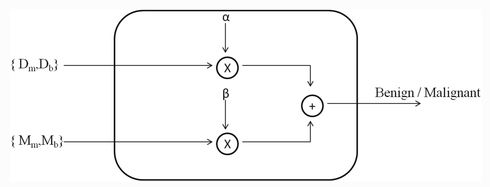
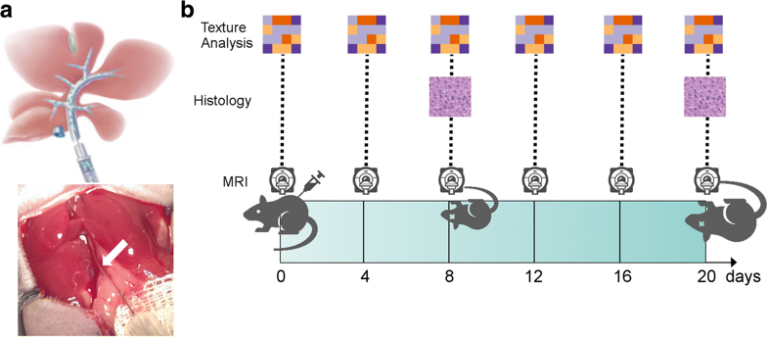
Machine learning classifiers vs. Experienced radiologists: Predicting Gleason pattern 4 prostate cancer
The authors of this study recognized the potential of multiparametric positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging (mpPET/MRI) for detecting and classifying breast lesions. To better understand computer-aided segmentation and diagnosis (CAD) features, the authors introduced a data-driven machine learning approach for a CAD system that enables the assessment of the relevance of mpPET/MRI features on segmentation and classification accuracy. Key points: