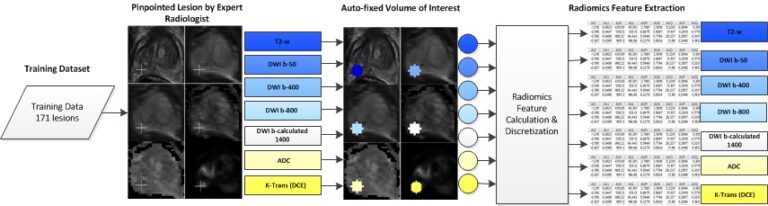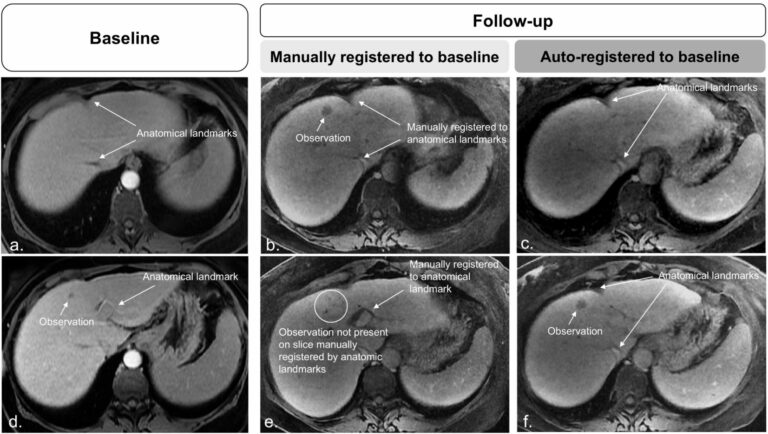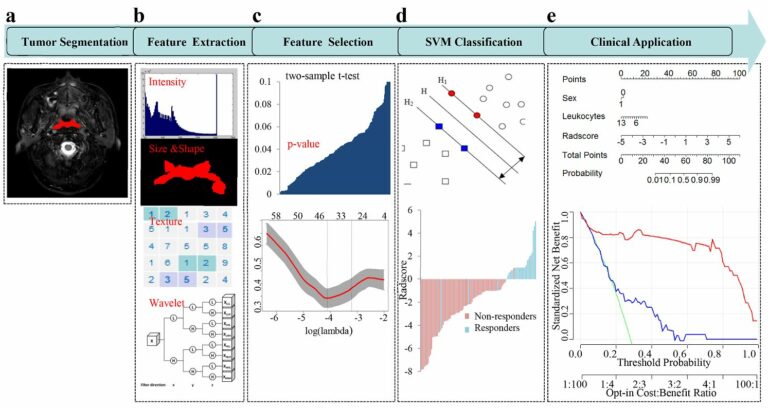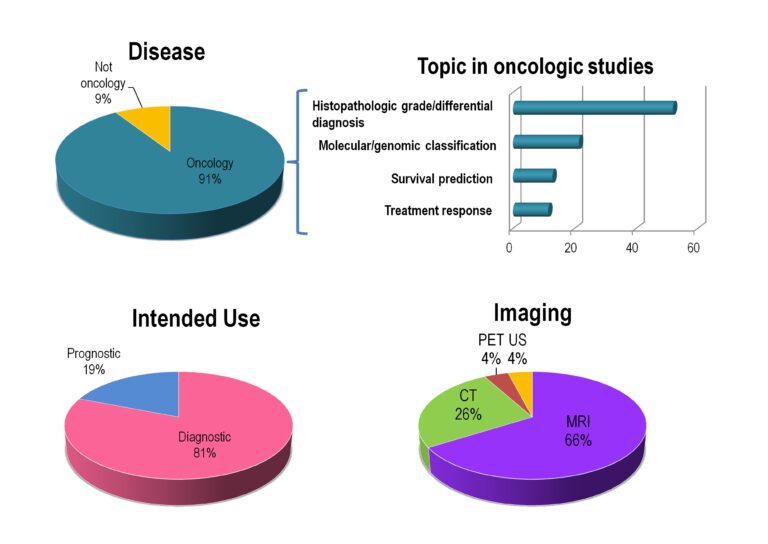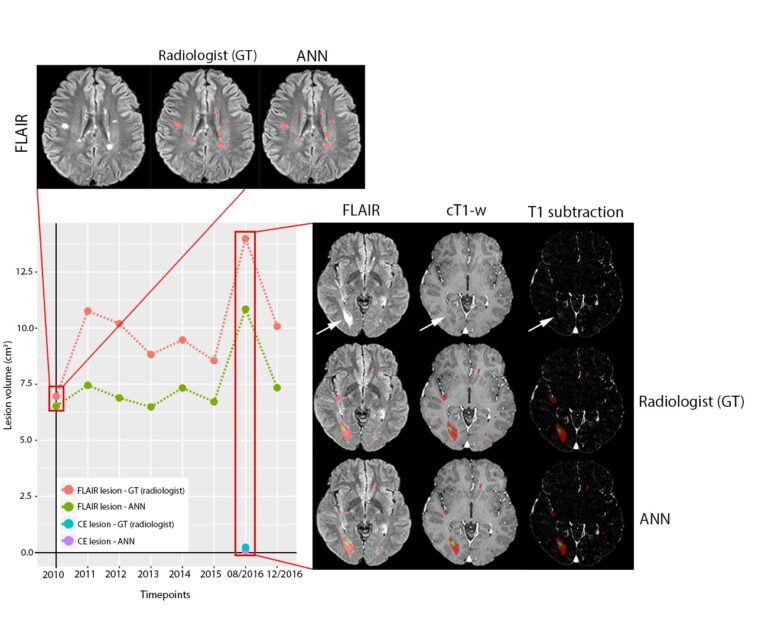
Automated volumetric assessment with artificial neural networks might enable a more accurate assessment of disease burden in patients with multiple sclerosis
Multiple automated methods for segmentation of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions have been developed over the past years, and the use of artificial neural networks (ANN) has recently generated many outstanding results in the public segmentation challenges. As we all know from our work as radiologists, the routine clinical practice is always conducted with an economical balance between optimal scan times