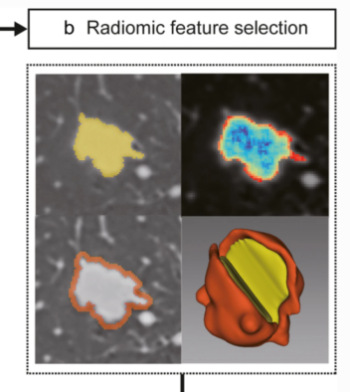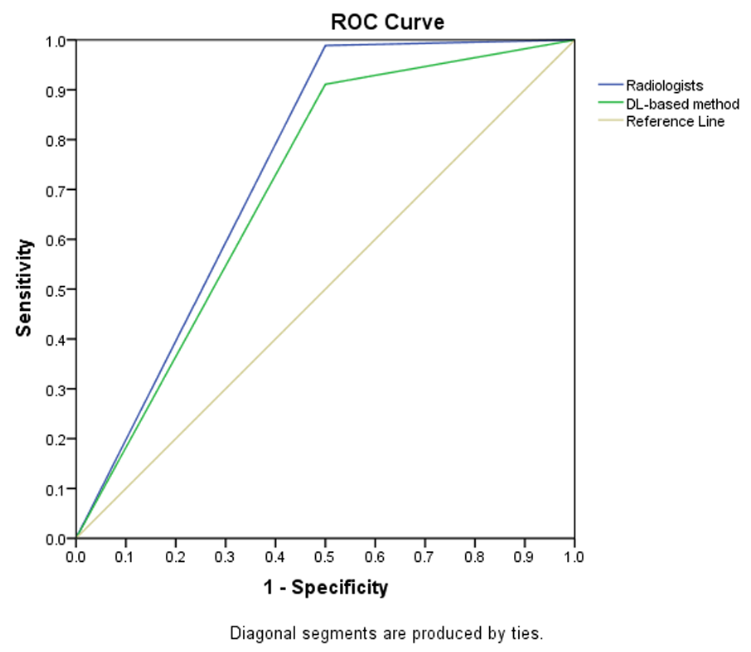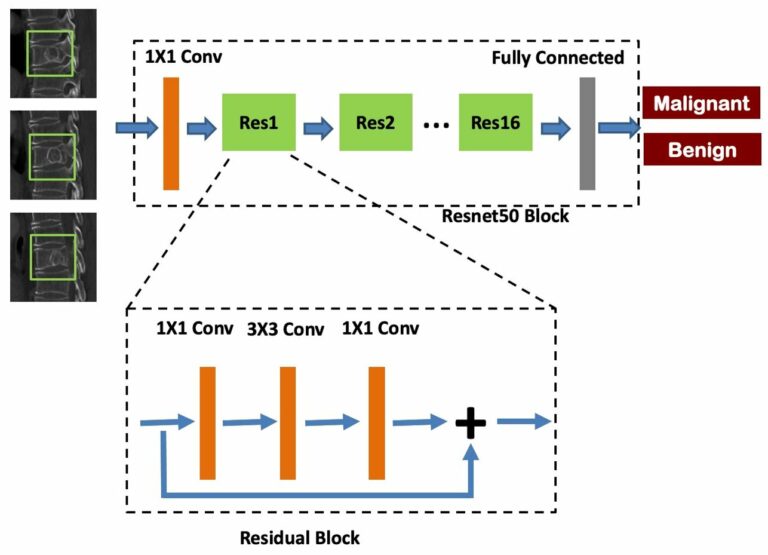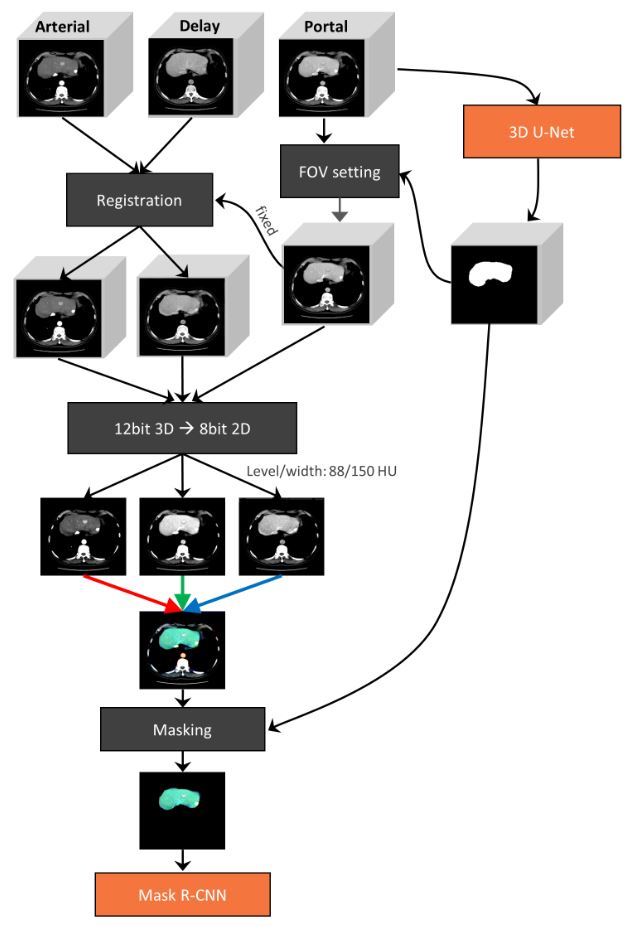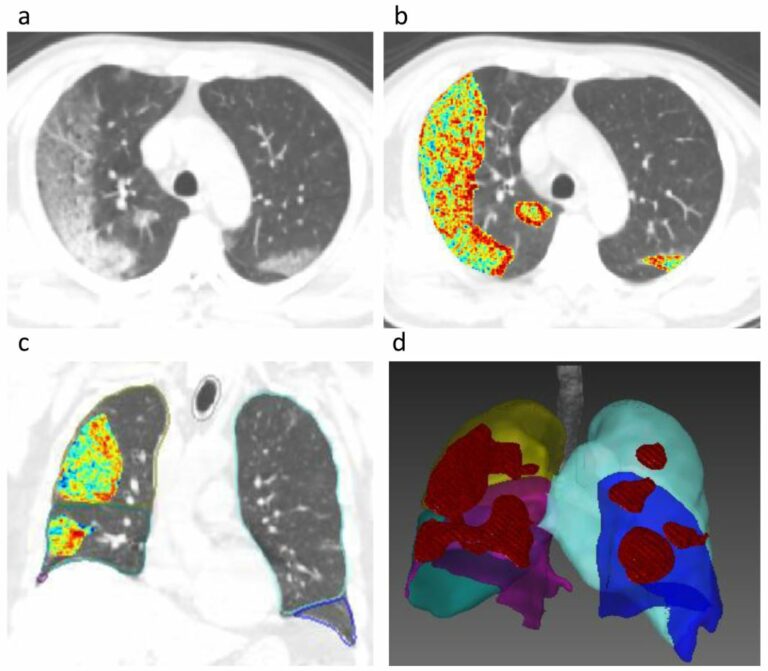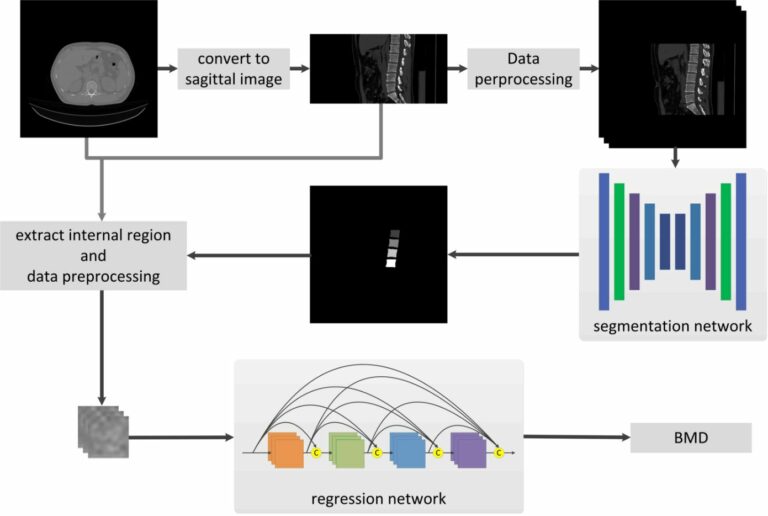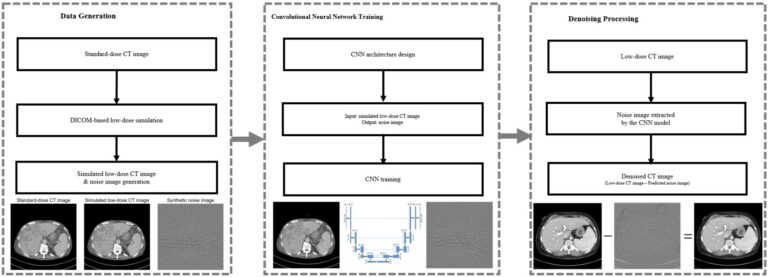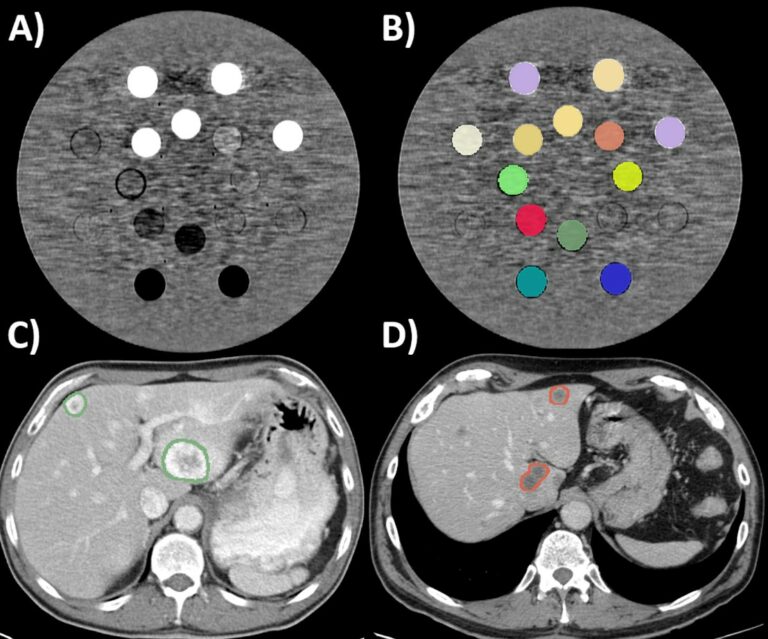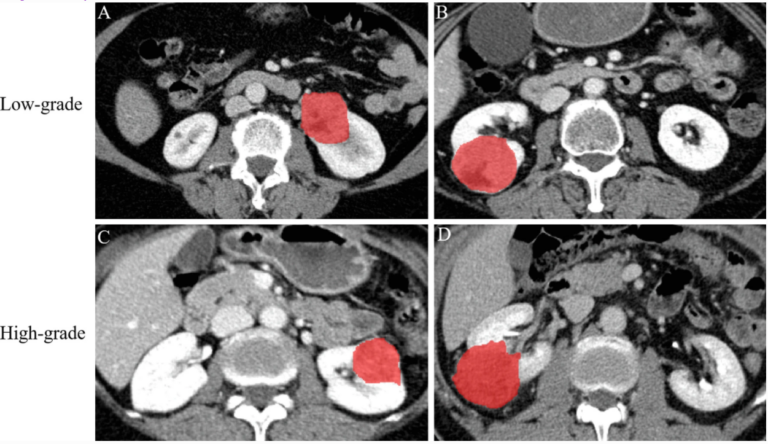
Can machine learning predict the WHO/ISUP nuclear grade of clear cell renal cell carcinomas?
In this retrospective study, the authors investigated if radiomics features extracted from nephrographic-phase (NP) CT images combined with clinicoradiological characteristics may have the potential to preoperatively differentiate between low- and high-nuclear grade of clear cell renal cell carcinomas (CCRCCs). They were able to demonstrate that radiomics analysis may be used as a potentially noninvasive method for distinguishing low- from high-grade