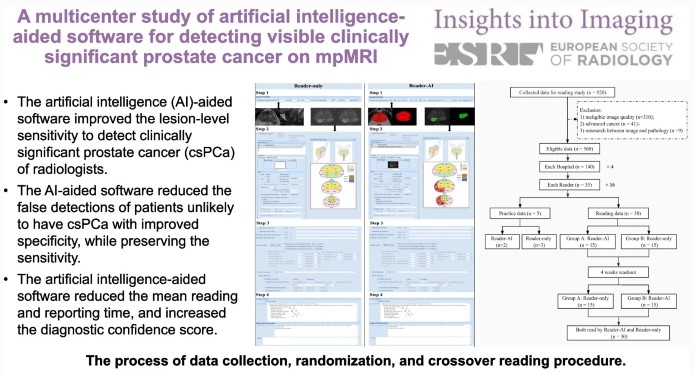
Intelligent noninvasive meningioma grading using deep learning
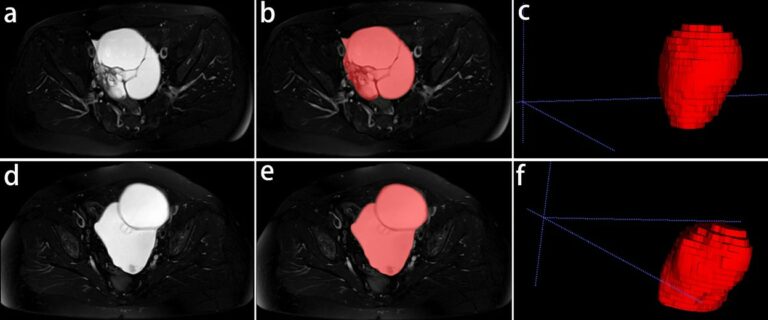
The purpose of this study was to establish a robust interpretable deep learning (DL) model for the automatic noninvasive grading of meningiomas along with segmentation. Over 250 meningioma patients who underwent a preoperative brain MRI, including T2-weighted (T2) and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (T1C) images, were included in the training set. The authors were able to determine that an interpretable multiparametric DL