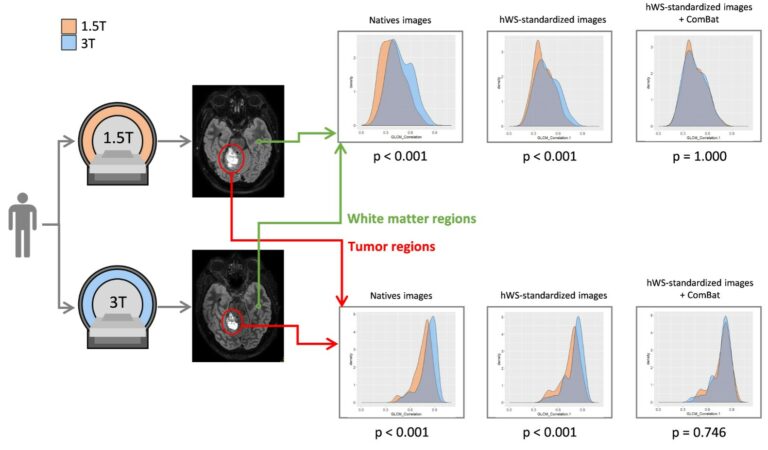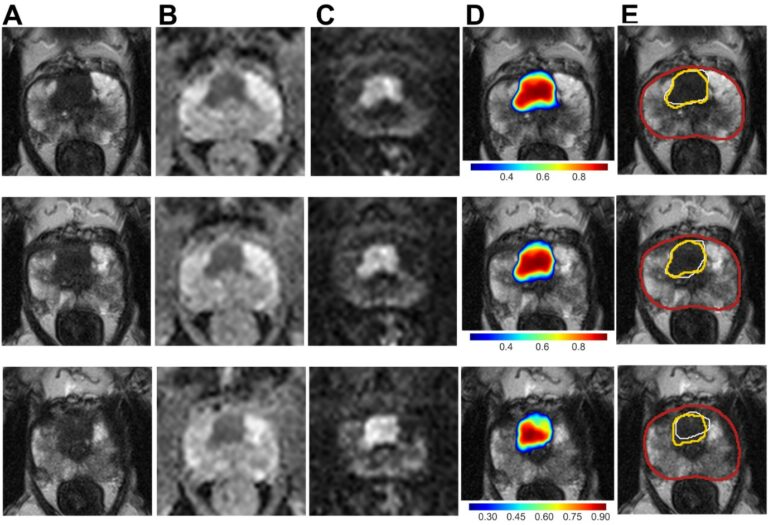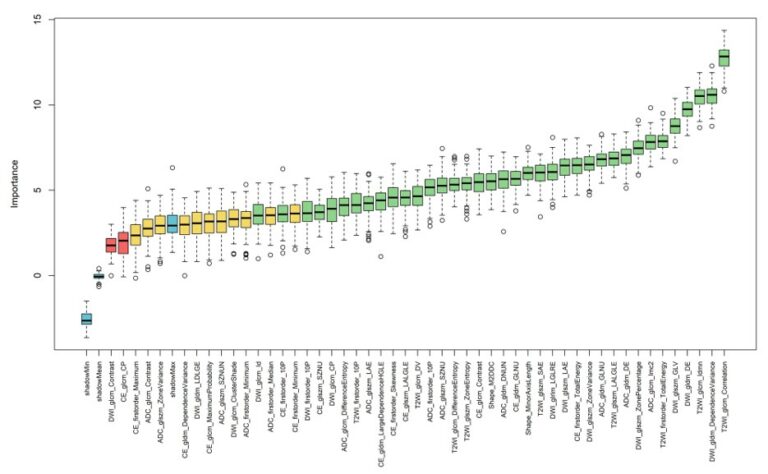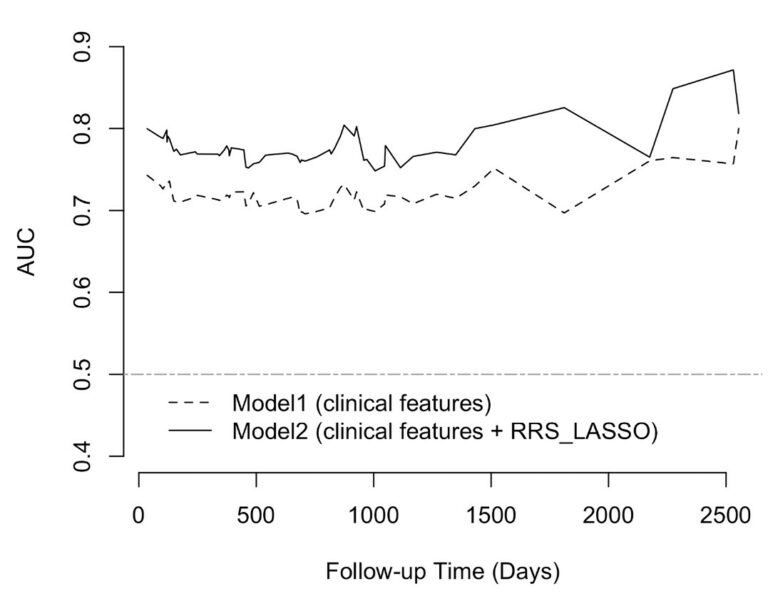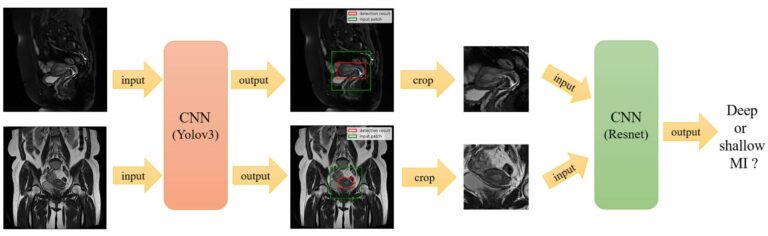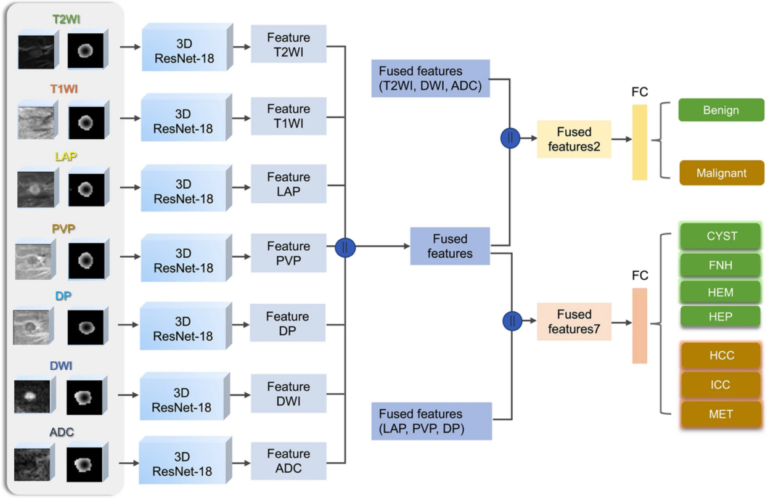
Saliency-based 3D convolutional neural network for categorising common focal liver lesions on multisequence MRI
We investigated a saliency-based 3D convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify seven categories of common focal liver lesions and validated the model performance. This retrospective study included 557 lesions examined by multisequence MRI. We found that this interpretable deep learning model showed high diagnostic performance in the differentiation of common liver masses on multisequence MRI. A few important notes on