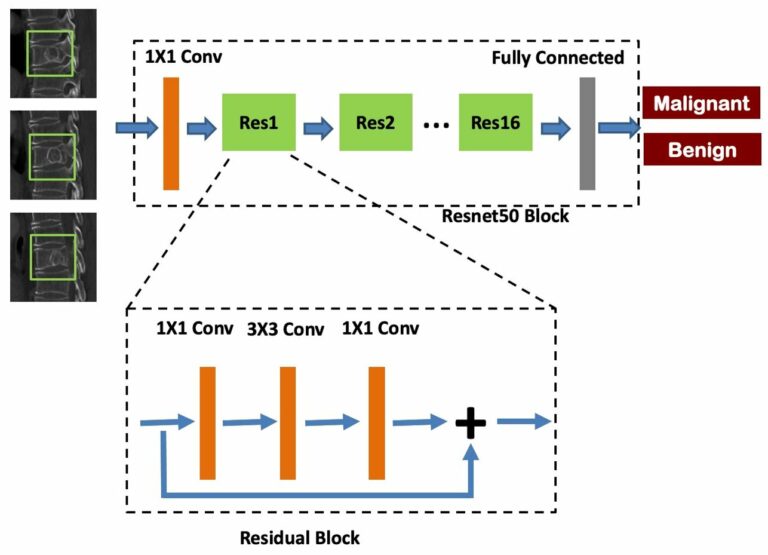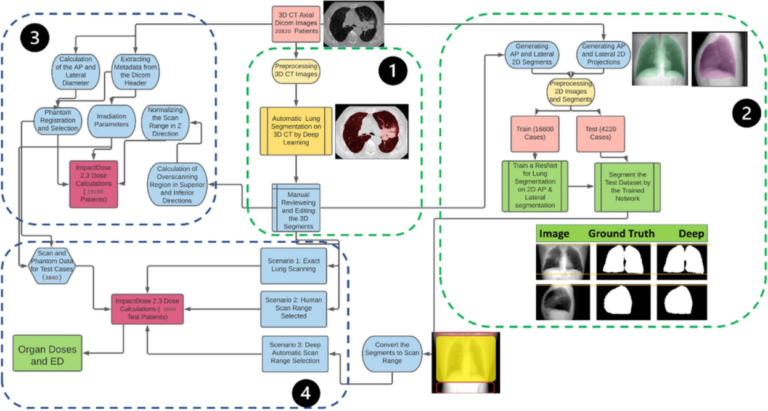
Deep learning assesses additional radiation dose in overscanning
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the number of chest CT examinations has dramatically increased, which will undeniably impact public medical exposure. Overscanning, i.e., scanning unnecessary regions in the axial field-of-view, causes noticeable excessive radiation dose to patients undergoing chest CT examinations. The manual procedure of selecting the scan range based on anterior-posterior or lateral localizers is prone to human error in