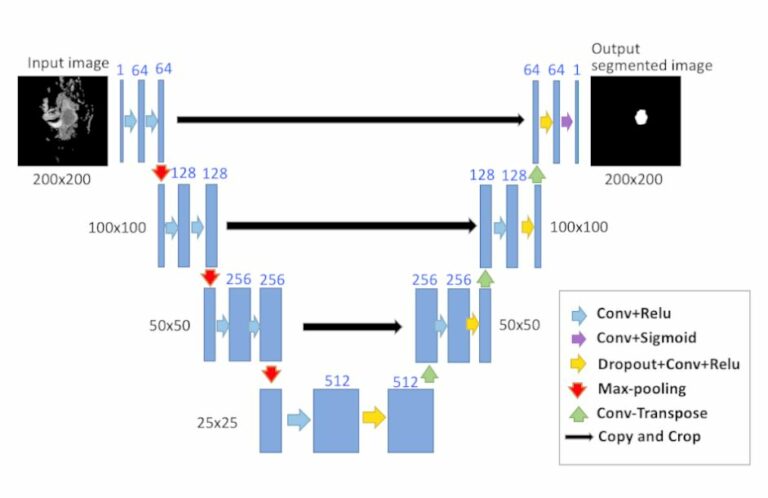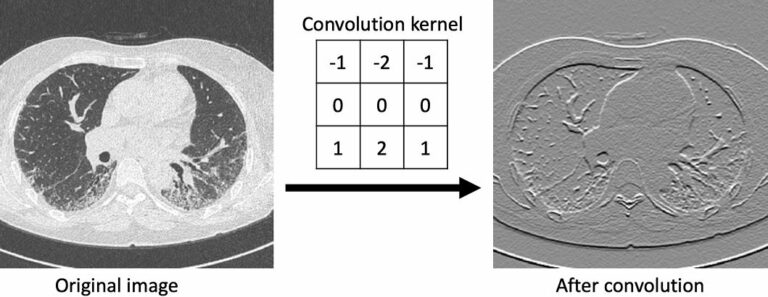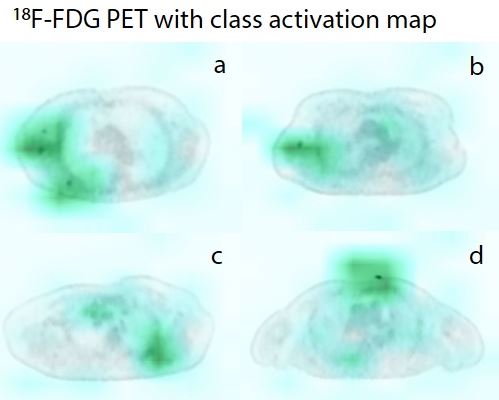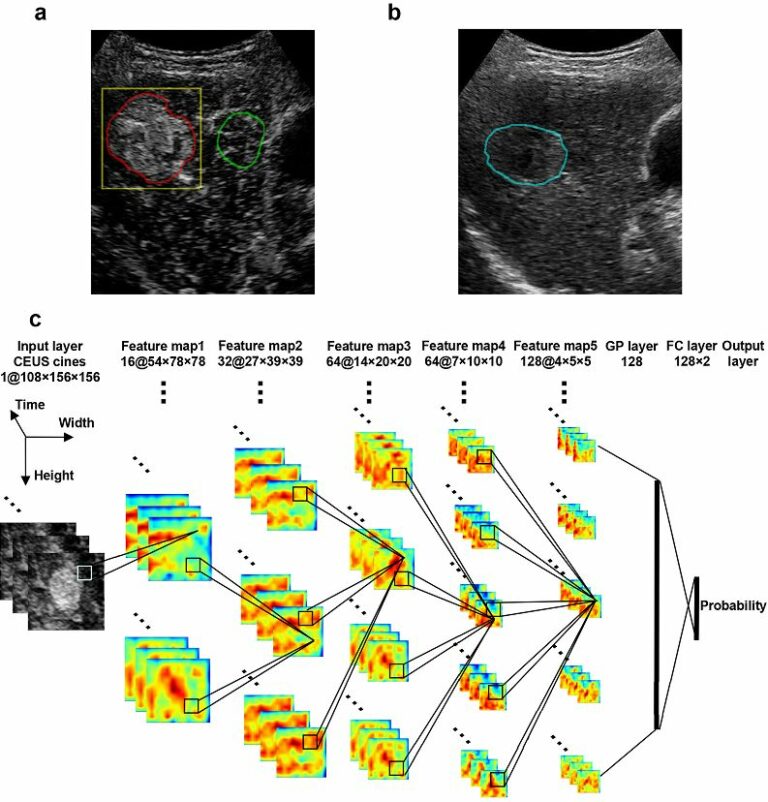
Automated identification of chest radiographs with referable abnormality with deep learning: need for recalibration
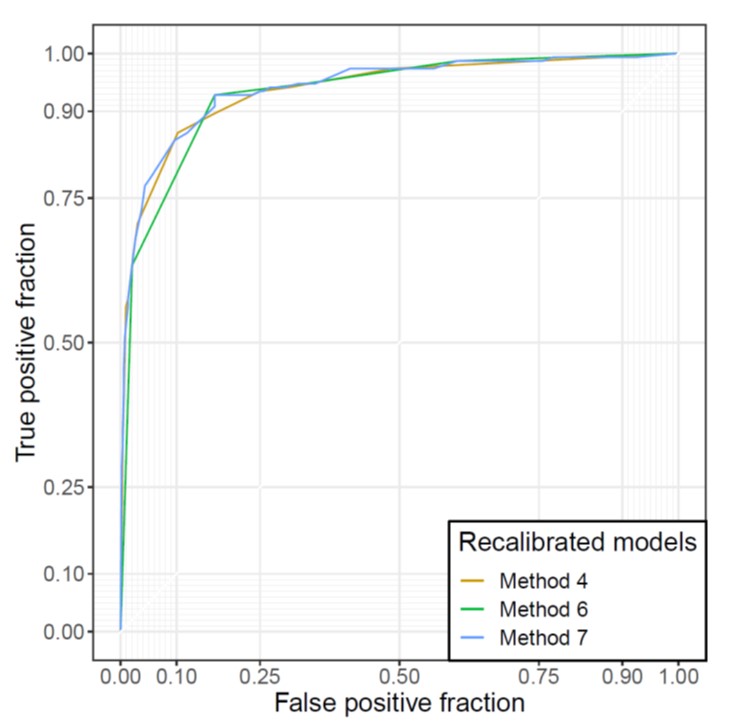
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the calibration of a deep learning (DL) model in a diagnostic cohort, as well as to improve the model’s calibration through recalibration procedures. The authors found that the calibration of the DL algorithm can be augmented through simple recalibration procedures, and improved calibration may enhance the interpretability and credibility of the model